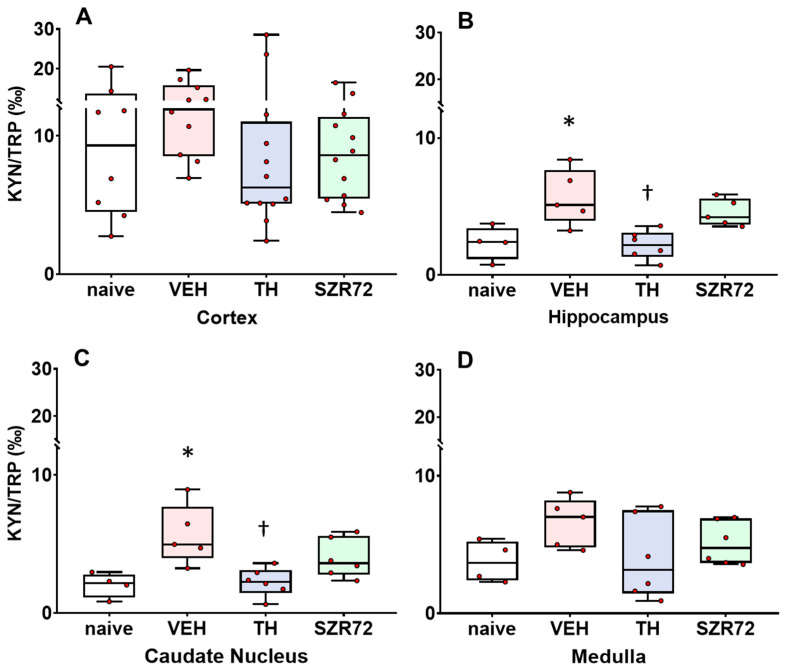
Figure 5.
Asphyxia-induced changes in brain kynurenine/tryptophan (KYN/TRP) ratios. Panel (A) shows cerebrocortical KYN/TRP ratios in the naive controls, as well as in the vehicle (VEH), hypothermia-treated (TH), and SZR72-treated (SZR72) groups subjected to asphyxia. Panels (B–D) show the values obtained from the hippocampus, the caudate nucleus, and the medulla, respectively. KYN/TRP ratios increased significantly after asphyxia in the hippocampus and the caudate nucleus, but a similar tendency could be observed in the other brain regions as well. Moreover, in the hippocampus and the caudate nucleus, TH reduced the KYN/TRP ratio back to control levels, while SZR72 did not have such a pronounced effect. Lines, boxes, and whiskers represent the median, the interquartile range, and the 10th–90th percentiles, respectively. *p < 0.05, * significantly different from the naive, † from the VEH group.