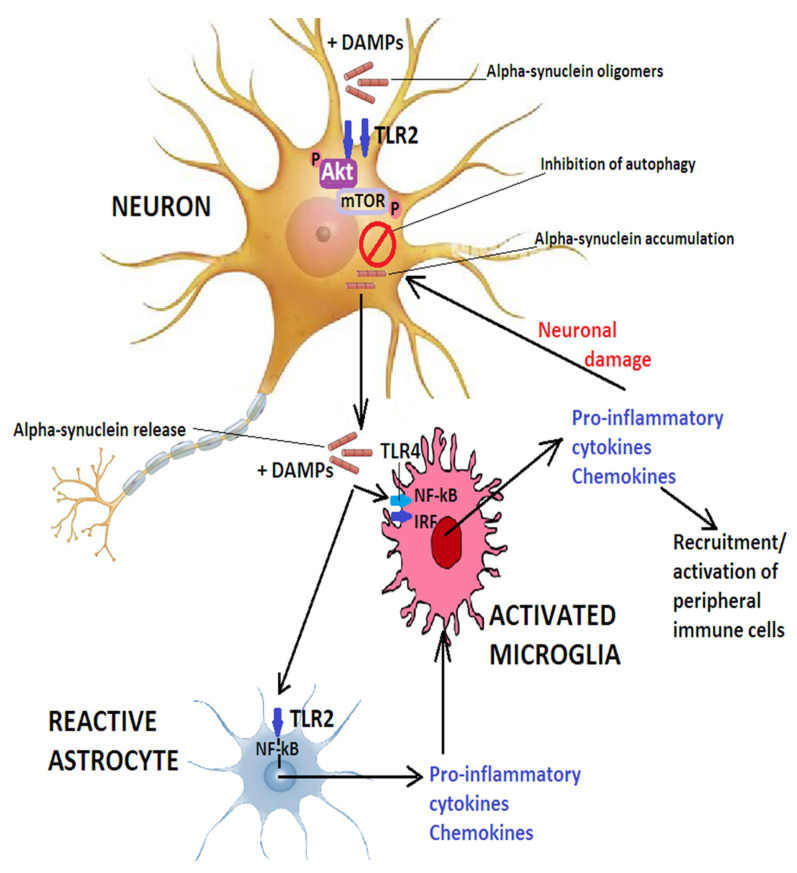
Figure 2.
The role of TLR2 and TLR4 in PD. Oligomeric α-synuclein or other DAMPs activate neuronal TLR2 and inhibit autophagy via the Akt/mTOR pathway. This inhibits α-synuclein clearance and causes the release of the misfolded protein which, together with other DAMPs, activate microglia via TLR2 and TLR4 and leads to translocation of IRF and NF-κB to the nucleus and secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines that exacerbate neuronal damage and may additionally recruit peripheral immune cells to the CNS. A-synuclein released by neurons, together with other DAMPs, also triggers astrocyte activation via TLR2 and induces the production of pro-inflammatory mediators which can further contribute to microglial activation. Abbreviations: DAMPs—damage-associated molecular patterns; IRF—interferon regulatory factor; NF-κB—nuclear factor kappa light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; TLR—toll-like receptor.