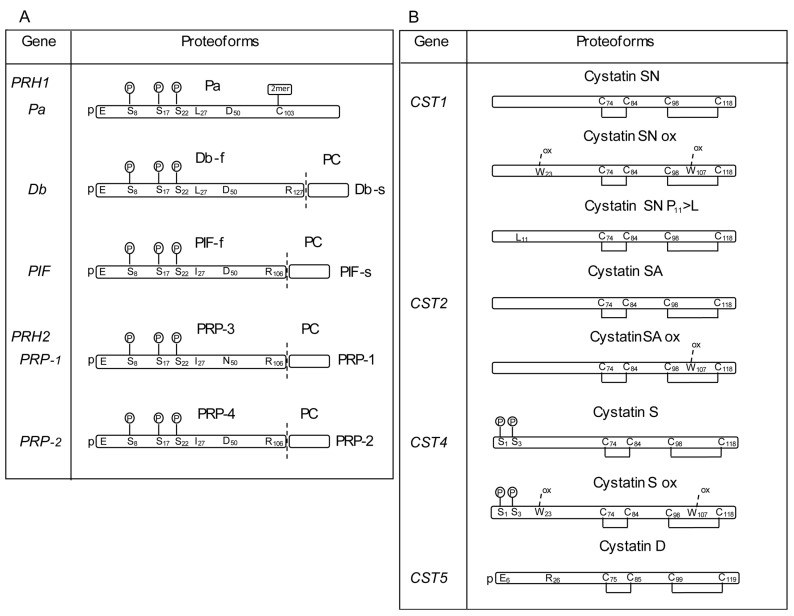
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of acidic proline-rich proteins (A) and cystatins (B). For each protein, the genetic allelic variants (S, small; M, medium; L, large; and VL, very large) are shown on the left-sided column; the resulting alternative proteoforms are shown on the right-sided column as blocks with corresponding symbols on top. All cystatin alternative proteoforms feature two disulfide bridges (indicated by brackets between Cys), oxidation (ox), and phosphorylation (P) sites. Vertical dashed lines indicate the pro-protein convertase cleavage sites with corresponding Arg (R) residues’ positions. The P enclosed in a circle denotes phosphorylation sites; ox: oxidation sites; p-E: N-terminal pyroglutamic acid; aminoacidic substitutions are shown for selected isoforms. See text for additional details.