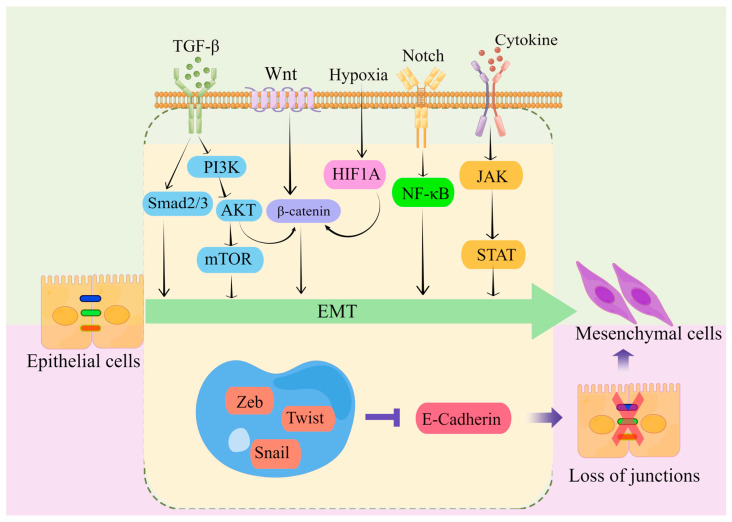
Figure 2.
Key pathways regulating EMT-TFs during EMT development in CRC [44,55,83,84,85,86,87]. There are several EMT-TFs (such as ZEB, SNAIL, and TWIST) that cooperate with signaling pathways in cells, and under the stimulation of factors such as TGF-β, Wnt, Notch, hypoxia, etc., repress genes related to epithelial status (such as E-cadherin), which leads to the loss of intercellular connections and allows epithelial cells to differentiate into a mesenchymal state. These transcription factors are pleiotropic, inducing a transition to a mesenchymal or partially mesenchymal cellular state. Abbreviations: EMT, epithelial–mesenchymal transition; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase; AKT, protein kinase B; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; HIF1A, hypoxia inducible factor 1 subunit alpha; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa B; JAK, janus kinase; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; ZEB, zinc finger E-box-binding homeobox.