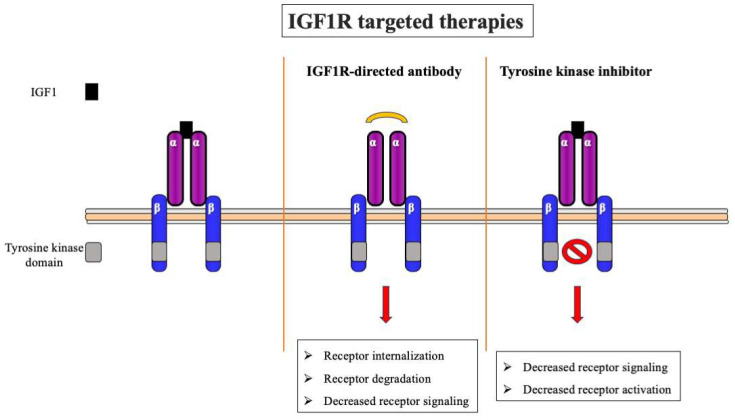
Figure 3.
IGF1R-targeted therapies. Schematic representation of two of the most common approaches for IGF1R targeting: anti-IGF1R monoclonal antibodies (center) and small-molecular-weight IGF1R tyrosine kinase inhibitors (right). Blocking of IGF1R by specific antibodies (usually against the extracellular domain) leads to a decrease in ligand binding and IGF1R activation with ensuing receptor internalization and degradation. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors abrogate IGF1R activation and signaling, without major effects on IGF1R expression.