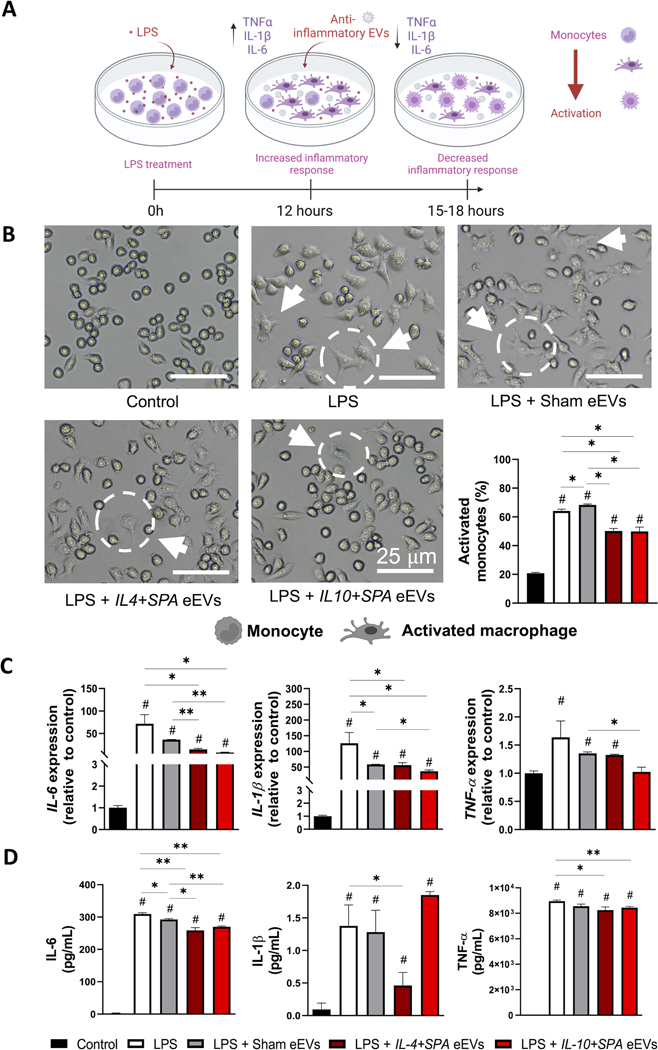
Fig. 2. Early post-treatment (3 hours) with IL-4+SPA and IL-10+SPA eEVs resolves activation and inflammation in LPS-challenged monocytes.
A) Schematic representation of the inflammatory response driven by RAW 264.7 monocyte cultures in vitro when treated with the endotoxin lipopolysaccharide (LPS), and the therapeutic effect of the post-treatment with anti-inflammatory eEVs to dampen the induced inflammation. B) Representative micrographs illustrating changes in cell morphology revealed that non-treated rounded monocytes get activated by the addition of the LPS, transitioning into a spindled shape typical of an activated or differentiated macrophage. Quantification analyses indicate that cell cultures treated with IL-4+SPA and IL-10+SPA EVs have less activated monocytes compared to the LPS and sham eEV groups. C) qRT-PCR analyses showed increased expression of IL-6, IL1-β, and TNF-α compared to the control (no LPS), and a decreased expression of IL-6, and IL1-β when treated with IL-4+SPA and IL-10+SPA eEVs. D) IL-6 and TNF-α protein expression was reduced when treated with both eEVs, and IL1-β with just IL-4+SPA eEVs. (n=3) All error bars are shown as SEM. *p<0.05 and **p<0.001, #significant difference with respect to the control with a p-value<0.05, One-way ANOVA.