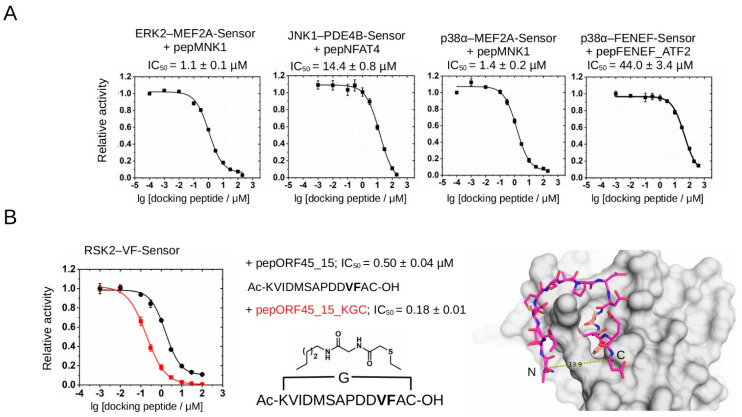
Figure 5.
Validation of different PhALC assays with kinase-docking-blocking peptides. (A) Summary of PhALC IC50 measurements with known D-motif peptides (pepMNK1 or pepNFAT4) or F-motif peptide (pepFENEF_ATF2). (B) Comparison of RSK2–VF-Sensor IC50 measurements with a linear (pepORF45_15; black) or a cyclic ORF45 (pepORF45_15_KGC; red) peptide. “Ac” and “OH” denote acetylated N-terminus and free carboxyl group at the C-terminus of the peptides, respectively. The chemical formula shows the structure of the artificial linker, with a glycine (G) inserted between the side chains of the N-terminal lysine and the C-terminal cysteine, thus making a circular peptide. The panel on the right highlights the close proximity of the N- and C-termini of a 15mer from the bound ORF45 peptide from the crystal structure of the RSK2(NTK)-pepORF45 crystallographic complex (PDB ID: 7OPO). This panel also shows how the VF-motif (colored in salmon) binds into a small hydrophobic pocket on the RSK(NTK). Note that in the ORF45_15 peptide the original Thr and Glu amino acids at the N- and C-termini were replaced with Lys and Cys to able to link them (~14 Å) via their side chains covalently (pepORF45_15_KGC). Error bars show SD based on three measurements.