Figure 9.
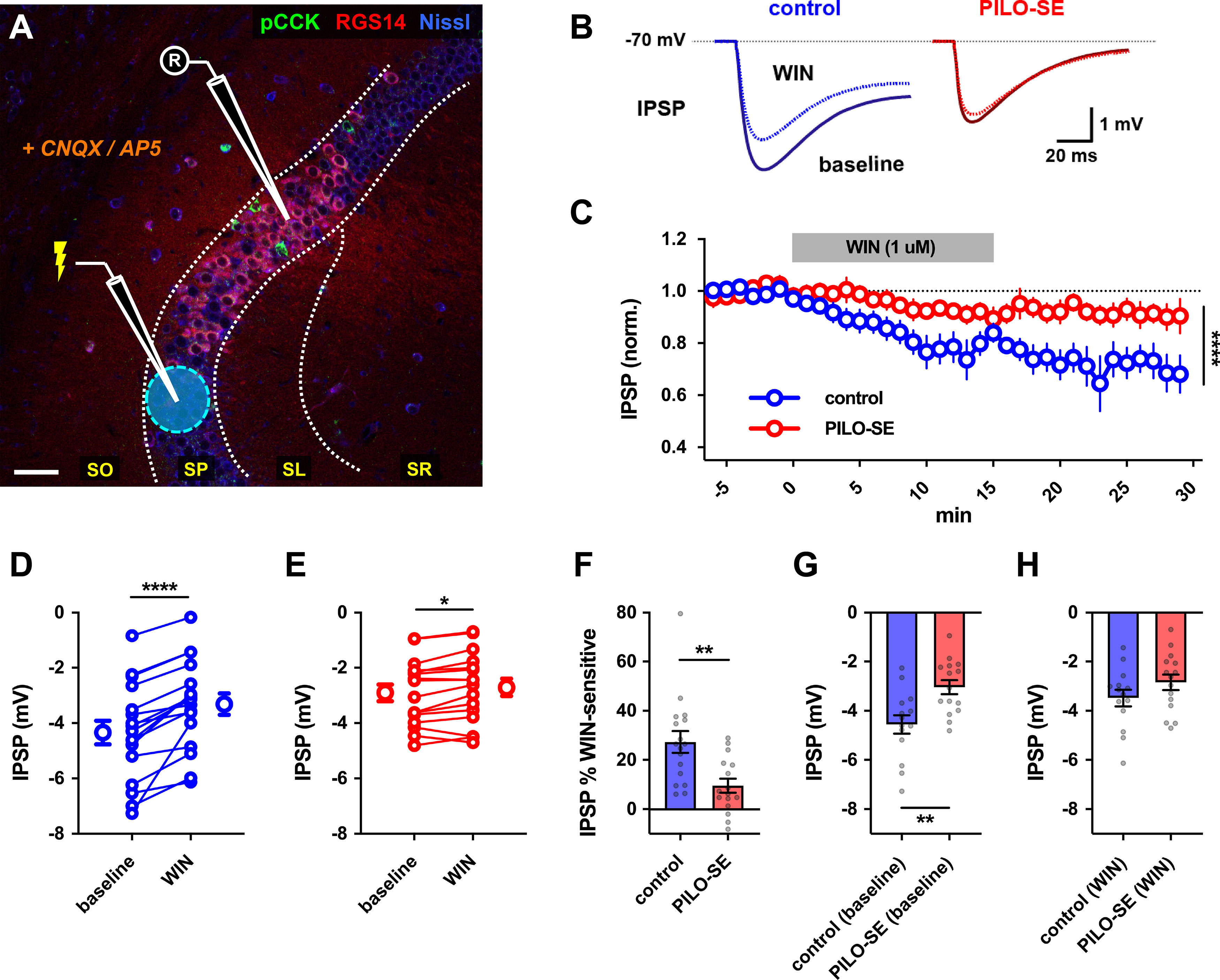
Reduced contribution of CCK+ interneurons to inhibition of CA2 PNs in PILO-SE. A, A representative image illustrating the experimental configuration using electrical stimulation in SP to evoke monosynaptic IPSPs in CA2 PNs (excitation blocked with CNQX and d-APV). Scale bar, 60 µm. B, Representative averaged IPSPs from control (blue) or PILO-SE (red) CA2 PNs before and 11–25 min after application of WIN (1 μm). C, Time course of normalized IPSP amplitude following WIN application in CA2 PNs from control and PILO-SE mice. D, E, IPSPs before and 11–25 min after application of WIN in control (D) and PILO-SE (E) mice. Each pair of points is from one cell in separate slices. F, The percentage reduction of the IPSP (relative to baseline) in control mice was significantly greater than in PILO-SE mice). G, The baseline (pre-WIN) IPSP amplitude in CA2 PNs from control mice was significantly larger in amplitude than the baseline IPSP amplitude in PILO-SE cells. H, There was no significant difference between the post-WIN IPSP amplitude in CA2 PNs from PILO-SE mice and the post-WIN IPSP amplitude in control cells.
