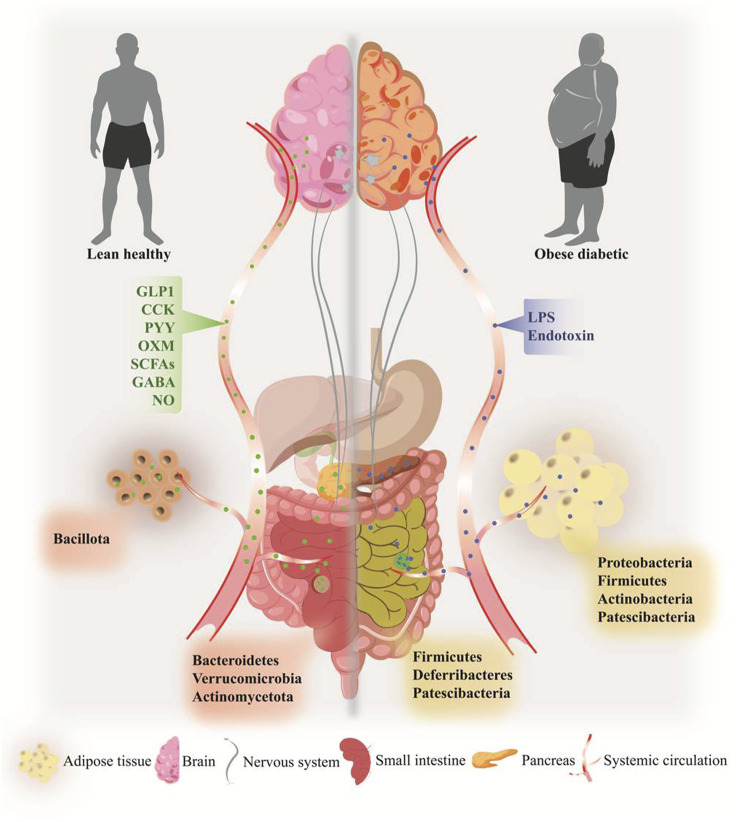
FIGURE 1.
Overview of obesity-induced dysbiosis and associated pathogenesis in the gut, gut-brain axis, pancreas, and adipose tissue of type 2 diabetes. Specific microbial phyla signatures were observed in gut and adipose tissue in the onset of obesity-induced T2D (right side) compared to lean healthy individual (left side). A Plethora of gut microbiome-derived metabolites participates in organs function, including gut-brain homeostasis, pancreas function, and inflammatory homeostasis. Alteration of microbial metabolites including LPS, endotoxins, and MAMPs leads to the development of pathophysiological state in obesity and T2D, by rapid systemic inflammation, releasing pro-inflammatory molecules, gut-brain dysfunction, and pancreatic damages.