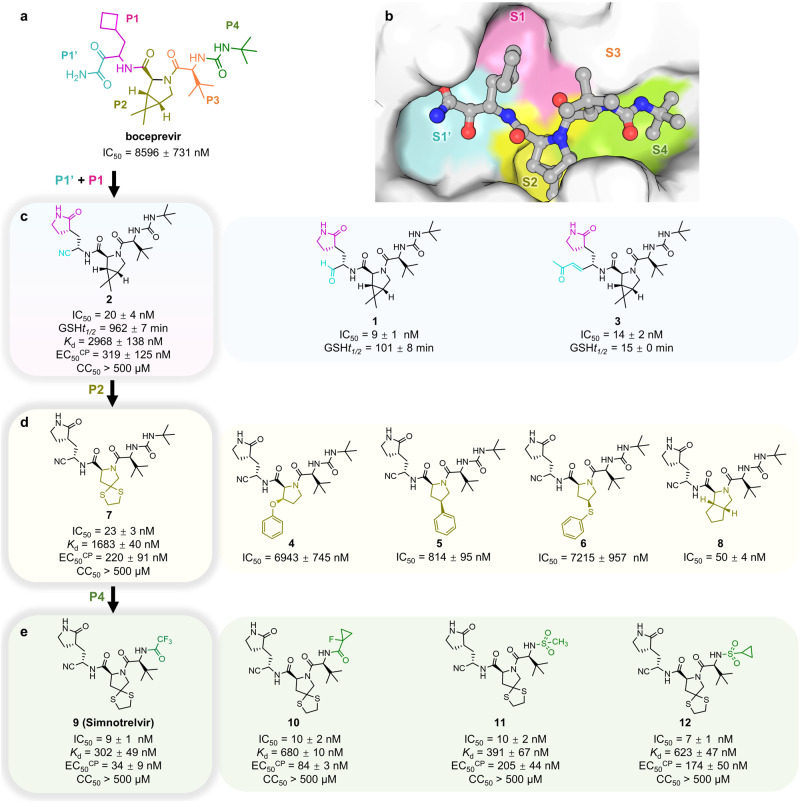
Fig. 1. Design strategy, chemical structures, and in vitro biochemical and antiviral activities of SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro inhibitors.
a The chemical structure of boceprevir and its inhibitory activity against SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro (expressed as IC50). P1’-P4 segments of boceprevir are colored in cyan, magenta, olive, orange, and green, respectively. b Molecular surface representation of boceprevir interacting with the S1ʹ-S4 subsites of SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro (PDB code: 6XQU). Boceprevir is shown in gray balls and sticks. The S1’-S4 subsites are colored cyan, magenta, yellow, orange, and green, respectively. c–e Chemical structures and in vitro biochemical and biophysical characterization of compounds that were designed to favorably interact with the S1’(C145) and S1 (c), S2 (d) and S4 (e) subsites of SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro. IC50 is the half-maximal inhibitory concentration of the compound against the protease determined by the enzymatic inhibition assay. Kd is the dissociation constant of the compound from the C145G mutant 3CLpro measured by ITC. GSHt1/2 is the half-life of the electrophile warhead to react with glutathione. EC50CP and CC50 are the half-maximal effective concentration in the presence of the P-glycoprotein efflux inhibitor CP-100356 and the half-maximal cytotoxic concentration of the compound in Vero E6 cells, respectively. Three independent experiments were performed to determine the IC50, GSHt1/2, Kd, EC50CP, and CC50 values.