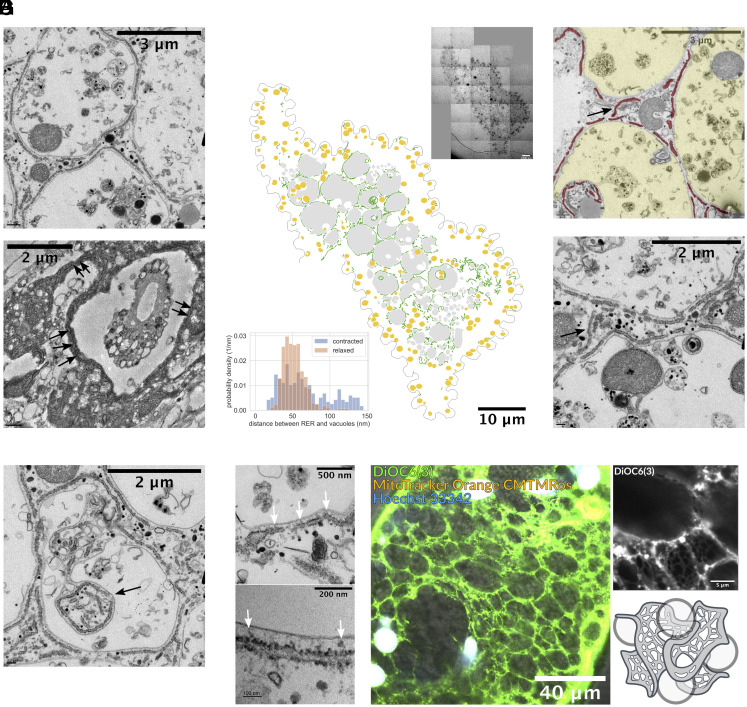
Fig. 2.
Intimate spatial relationship between RER and vacuolar meshwork. (A) TEM imaging of S. ambiguum before (Upper) and after (Lower) ultrafast contraction shows the vacuolated cytoplasm, and the RER is intimately wrapping around the vacuoles in both cases. Refer to SI Appendix, Fig. S1 for low magnification images. (B) Cross-section montage of a relaxed organism and its segmentation of RER (green), vacuoles (gray), and mitochondria (yellow). The entangled topology between RER and vacuoles spans the entire cross-section, not limited to a specific region. The inset on the upper right corner shows the original image. Width of original image: 65.287 m. The histogram on the lower left corner shows the distance between RER and nearby vacuoles in contracted and relaxed organisms under TEM. In the relaxed organism, the distance ranges from 30 to 70 nm (343 measurements, mean s td: 51.9 14.6 nm), while in the contracted organism, this distance becomes more variable but remains below 150 nm (269 measurements, mean std: 82.1 52.9 nm). (C) TEM occasionally reveals the “bridging” RER (arrows) that connects the RER of two nearby vacuoles. This is expected as RER is a continuous lumen. RER is false colored in red and vacuoles in yellow on the Top figure. (D) Extreme tram-tracking of RER along the contour of vacuoles was observed, even when cytoplasm invaginated inward to the vacuoles (arrows). (E) At higher magnification, we can see some materials (white arrows) that might be the protein connections between RER and vacuoles. (F) Confocal imaging of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and vacuolar meshwork of a contracted organism (Left) and a cropped magnified region (Upper right). Note that the image is a longitudinal section. The image shows a fenestrated web-like structure of ER wrapping around vacuolar meshwork throughout the entire organism. Refer to Movies S3–S5 for complete z-stack video. (G) 3D schematic drawing illustrating the entangled topology between fenestrated ER and vacuoles.