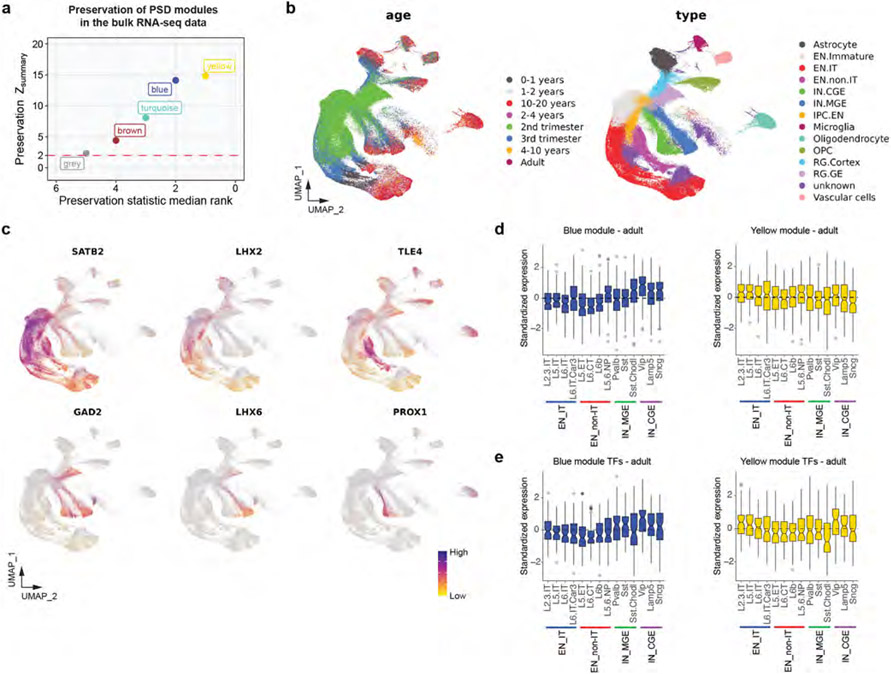
Extended Data Fig. 6 ∣. Transcription of PSD proteins.
a, Preservation of human PSD modules in the bulk RNA-seq data. b, Uniform manifold approximation and projection (UMAP) plots showing the distribution of age groups and cell types in the single-nucleus RNA-seq data from developing human neocortex. c, UMAP plots showing the expression patterns of neuronal subtype-specific markers in the single-nucleus RNA-seq data from developing human neocortex. d, Standardized expression values of genes in the blue (n = 301 genes) and yellow (n = 218 genes) modules in individual neuronal subtypes of the adult human neocortex. Boxplot center: median; hinges: the 25th and 75th percentiles; whiskers: 1.5 × inter-quartile range. e, Standardized expression values of top TFs predicted to regulate the blue (95 genes) and yellow (97 genes) modules in individual neuronal subtypes of the adult human neocortex. Boxplot center: median; hinges: the 25th and 75th percentiles; whiskers: 1.5 × inter-quartile range. EN_IT, excitatory intratelencephalic neuron; EN_non-IT, excitatory non-intratelencephalic neuron; IN_MGE, inhibitory neuron derived from the medial ganglionic eminence; IN_CGE, inhibitory neuron derived from the caudal ganglionic eminence.