Fig. 2 |. Single-neuron encoding of choice and value during the 500-ms preceding choice.
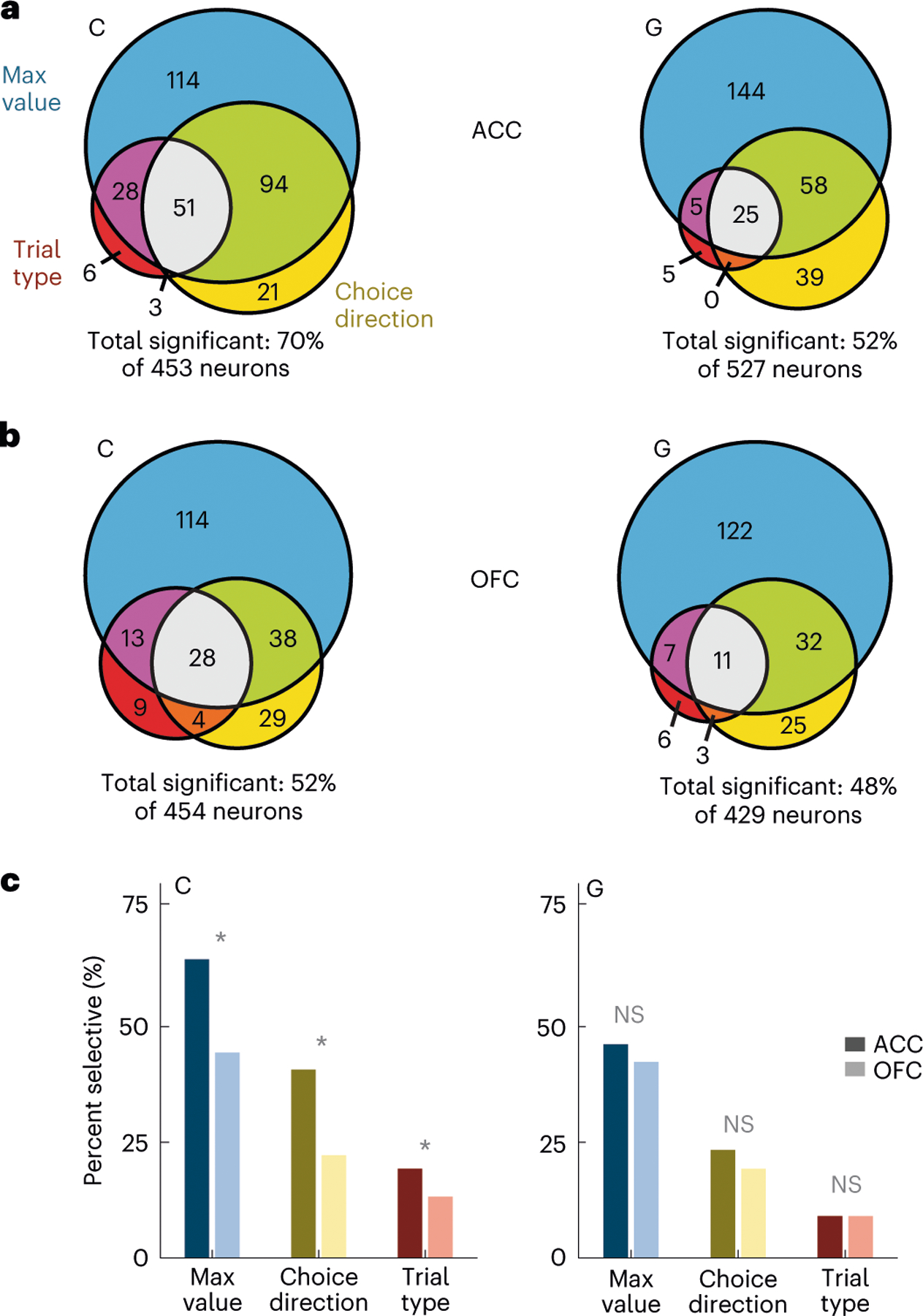
a, ACC firing rates were modeled via linear regressions as a linear combination of the maximum value (blue), choice direction (yellow) and trial type (red) in overlapping 100-ms windows stepped by 25 ms. Most neurons were significantly predicted by at least one factor. Significance was defined as P < 0.01 for at least 100 ms. Statistical tests were two-sided. b, Same as a but for OFC neurons. c, Comparison of the prevalence of different types of encoding between ACC and OFC. In subject C, selective neurons were more common in ACC than in OFC, but there was little difference in subject G. Asterisks indicate significant differences ( test, P < 0.01). NS, not significant.
