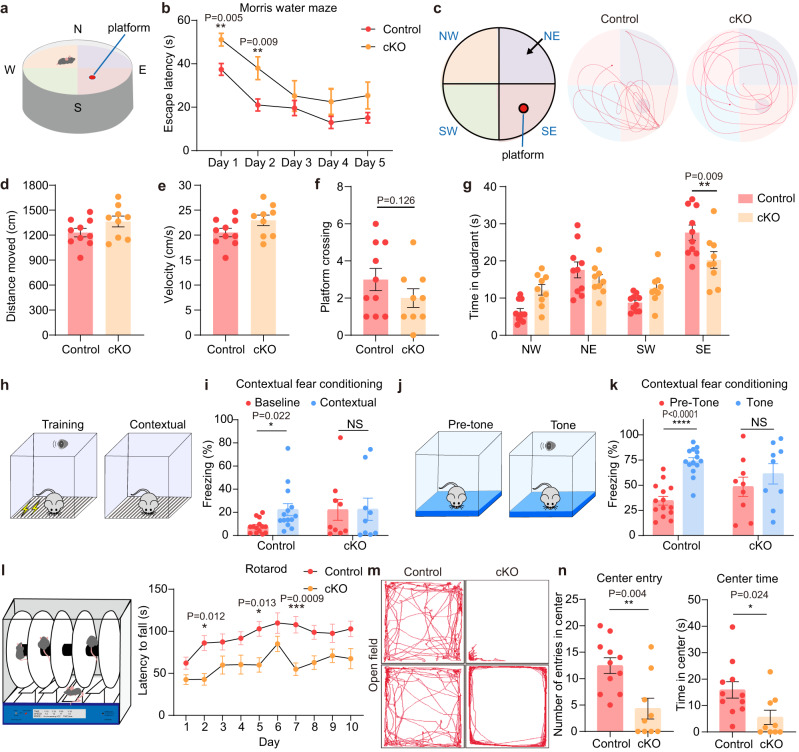
Fig. 2. Kdm2bEmx1-ΔCxxC mice exhibit defects in spatial memory, contextual fear conditioning, and motor learning.
a Diagram of the Morris water maze test. b Latency to find the hidden platform across training period in the Morris water maze test. c An overhead view of the Morris water maze, and representative swim paths of control mice and Kdm2bEmx1-ΔCxxC mice during the probe trial. The platform was set in the SE quadrant. d, e Distance moved (d) and velocity (e) during the probe trial (platform removed). f Frequencies of platform crossing during the probe trial. g Time spent in each quadrant during the probe trial. h, i The proportion of freezing time in context before training (Baseline) and after training (Contextual). j, k The proportion of freezing time in a new context before tone (Pre-Tone) and after tone (Tone). l Latency to fall during the rotarod test. m Representative traces of control and Kdm2bEmx1-ΔCxxC mice in the open-field arena. n Quantification of number of entries in center, and time spent in the center in the open-field test. Data are represented as means ± SEM. Statistical significance was determined using two-way ANOVA followed by Sidak’s multiple comparisons test (b, g, i, k, l), or using an unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test (d–f, n). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001; NS, not significant. n = 10 in (a–g), n = 14 in (h–k), n = 11 mice in (l–n) for control and n = 9 mice for Kdm2bEmx1-ΔCxxC.