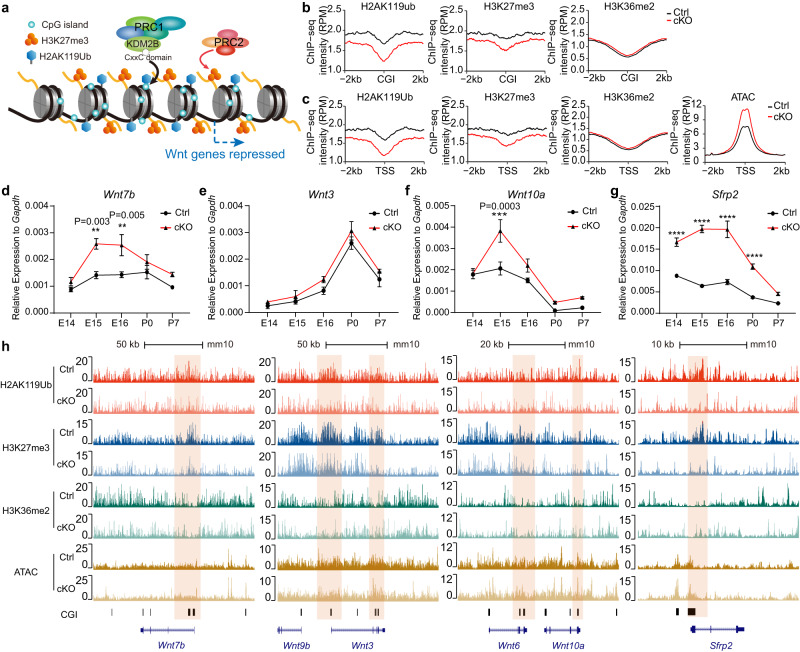
Fig. 6. KDM2B epigenetically silences components of Wnt signaling genes in developing hippocampi.
a The working diagram of KDM2B: KDM2B-CxxC recognizes and binds to CpG islands (CGI) of DNA, therefore recruiting the PRC1 to CpG islands (CGIs). Reciprocal recognition of modifications by PRC1 and PRC2 leads to enrichment of H2AK119ub and H3K27me3, hence stabilizing gene repression. b Line charts showing average H2AK119ub, H3K27me3 and H3K36me2 signals at CGIs (±2 kb flanking regions) in P0 control (black lines) and Kdm2bEmx1-ΔCxxC (cKO) (red lines) hippocampi. c Line charts showing average H2AK119ub, H3K27me3, H3K36me2 and ATAC-seq signals at CGI + TSS (±2 kb flanking regions) in P0 control (black lines) and Kdm2bEmx1-ΔCxxC (cKO) (red lines) hippocampi. TSS transcription starting sites. d–g RT-qPCR showing relative expressions of Wnt7b, Wnt3, Wnt10a and Sfrp2 in control (black lines) and Kdm2bEmx1-ΔCxxC (red lines) hippocampi of indicated developmental stages (E14.5, E15.5, E16.5, P0 and P7). h The UCSC genome browser view of HA2K119ub, H3K27me3, and H3K36me2 enrichment and ATAC-seq signal in P0 control and Kdm2bEmx1-ΔCxxC (cKO) hippocampi at Wnt gene loci [corresponding to (d, f, g), Wnt7b, Wnt3, Wnt10a and Sfrp2]. CGIs were shown as black columns at the bottom, and signals represent ChIP-seq RPM (reads per million). Colored regions marked enrichment differences between control and cKO. For E14.5, n = 4 for control brains and n = 4 for Kdm2bEmx1-ΔCxxC brains; for E15.5, n = 3 for control brains and n = 3 for Kdm2bEmx1-ΔCxxC brains; for E16.5, n = 3 for control brains and n = 3 for Kdm2bEmx1-ΔCxxC brains; for P0, n = 2 for control brains and n = 4 for Kdm2bEmx1-ΔCxxC brains; for P7, n = 3 for control brains and n = 3 for Kdm2bEmx1-ΔCxxC brains (d–g). Data are represented as means ± SEM. Statistical significance was determined using two-way ANOVA followed by Sidak’s multiple comparisons test (d–g). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001.