Figure 1. Repeated ethanol injection suppresses somatodendritic GABABR-dependent signaling in BA principal neurons.
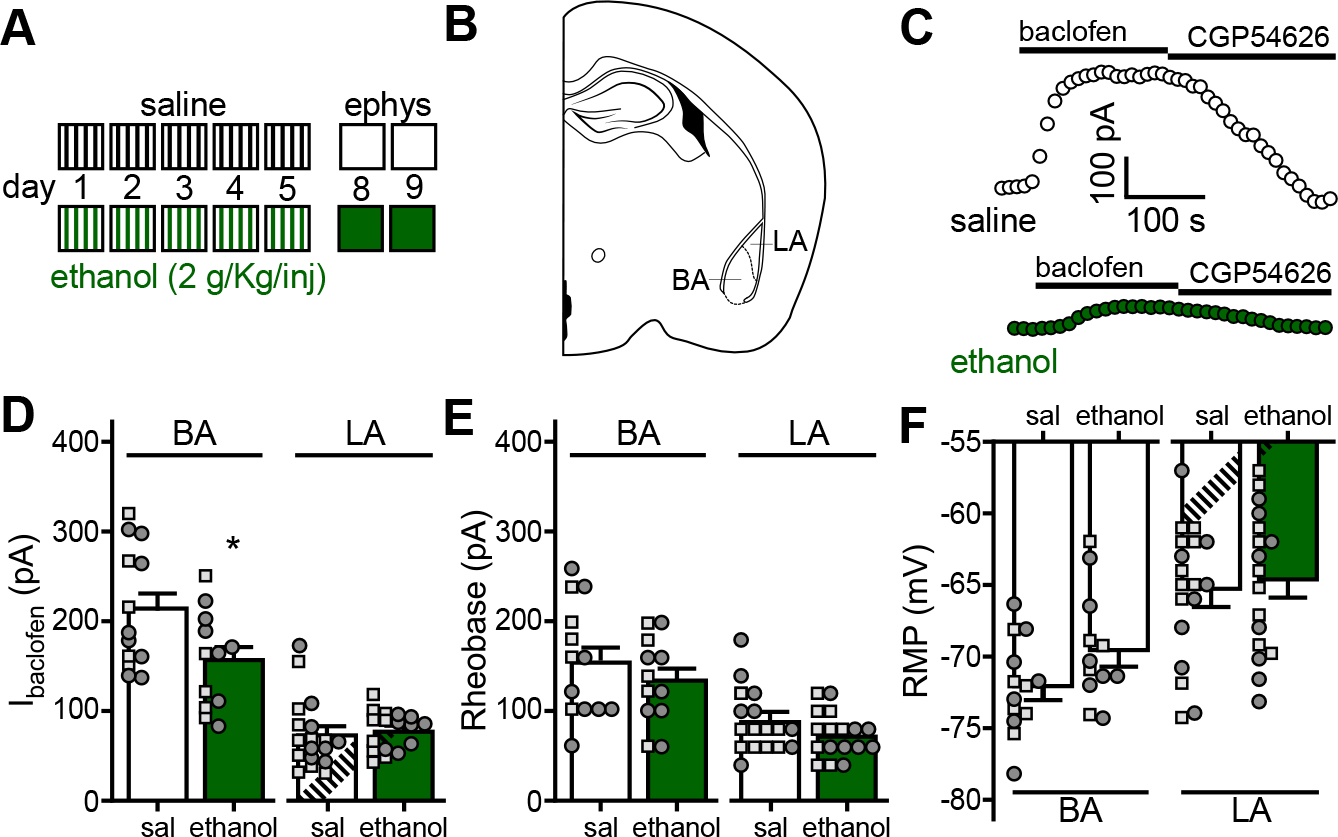
A. Depiction of the repeated ethanol injection protocol. C57BL/6J mice (34–41 d) were given 4 daily injections (1000, 1200, 1400, and 1600 h) of saline or ethanol (2 g/kg IP) over a consecutive 5-d period; injections are denoted by vertical lines. Electrophysiological analysis occurred on days 8 and 9.
B. Depiction of a coronal section containing the BLA, with BA and LA sub-regions highlighted.
C. Somatodendritic currents (Vhold = −60 mV) evoked by baclofen (200 μM) and reversed by the GABABR-selective antagonist CGP54626 (2 μM) in BA principal neurons, recorded 3 d after the last saline or ethanol injection.
D. Ibaclofen in principal neurons of the BA (t23=2.356, *P=0.0274; N=12–13/group; unpaired Student’s t-test) and LA (t26.81=0.375, P=0.711; N=17–18/group; unpaired Student’s t-test with Welch’s correction) from C57BL/6J mice treated with repeated saline (sal) or ethanol. Small squares and circles represent individual data points from male and female subjects, respectively.
E. Rheobase of principal neurons of the BA (t23=0.956, P=0.349; N=12–13/group; unpaired Student’s t-test) and LA (t33=1.527, P=0.136; N=17–18/group; unpaired Student’s t-test) from repeated saline- or ethanol-treated mice.
F. Resting membrane potential (RMP) of principal neurons of the BA (t23=1.823, P=0.0814; N=12–13/group unpaired Student’s t-test) and LA (t33=0.436, P=0.666; N=17–18/group; unpaired Student’s t-test) from repeated saline- or ethanol-treated mice.
