Figure 2. Chronic intermittent exposure to ethanol vapor suppresses somatodendritic GABABR-dependent signaling in BA principal neurons.
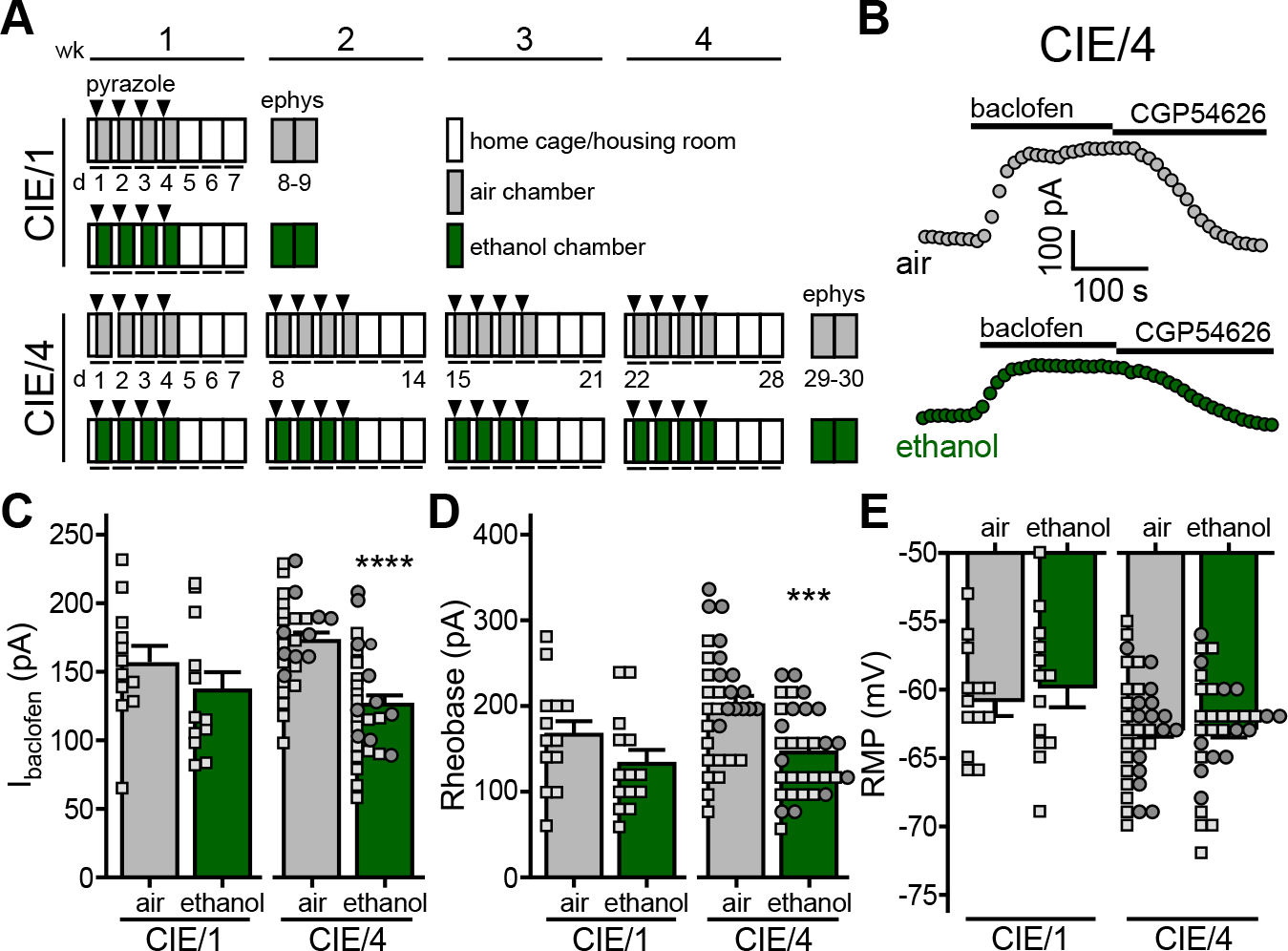
A. Depiction of chronic intermittent ethanol vapor exposure protocols. C57BL/6J mice (8 wk) were placed in ethanol vapor or air control chambers for 16 h sessions over 4 consecutive days, followed by 3 d of home cage housing. Prior to each session, mice were administered sodium pyrazole (68.1 mg/Kg IP; arrowheads) and either a priming dose of ethanol (1.5 g/Kg; 20% v/v) or saline (for air-treated controls). Separate cohorts of mice were run through 1-wk (CIE/1) and 4-wk (CIE/4) protocols, with electrophysiological assessments made 3–4 d after the final air or ethanol vapor exposure session.
B. Somatodendritic currents (Vhold = −60 mV) evoked by baclofen (200 μM) and reversed by CGP54626 (2 μM) in BA principal neurons from air- or ethanol-treated subjects following the CIE/4 protocol.
C. Ibaclofen in BA principal neurons from air- and ethanol-treated mice, 3–4 d after completing CIE/1 (t22=1.102, P=0.282; N=12/group; unpaired Student’s t-test) or CIE/4 (t58=5.072, ****P<0.001; N=30/group; unpaired Student’s t-test) protocols. Small squares and circles represent individual data points from male and female subjects, respectively.
D. Rheobase of BA principal neurons from air- and ethanol-treated mice, 3–4 d after completing CIE/1 (t25=1.523, P=0.140; N=13–14/group; unpaired Student’s t-test) or CIE/4 (t62=3.849, ***P=0.0003; N=32/group; unpaired Student’s t-test) protocols.
E. RMP of BA principal neurons from air- and ethanol-treated mice, 3–4 d after completing CIE/1 (t25=0.552, P=0.586; N=13–14/group; unpaired Student’s t-test) or CIE/4 (t65=0.0113, P=0.991; N=32–35/group; unpaired Student’s t-test) protocols.
