Figure 2.
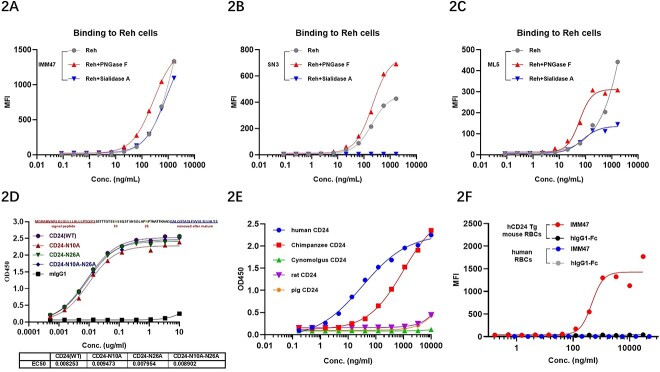
IMM47 binding to CD24 is independent of N-glycosylation and cross-reaction between different species’ CD24. (A-C) The extracellular domain of CD24 has 14 O-glycosylation and 2 N-glycosylation sites. N-glycosidase and sialidase-treated Reh cells had little effect on the affinity of IMM47 (A) and ML5 (C), and N-glycosidase-treated Reh cells even enhanced their binding ability; SN3 (B) can bind to Reh cells significantly, and the cells treated with sialidase cannot bind to SN3, indicating that sialylation of CD24 on Reh cells is crucial for SN3 binding. The result demonstrated that IMM47 binding to CD24 is independent of glycosylation modifications. (D) The extracellular domain’s N-glycosylation alterations had no effect on IMM47’s ability to bind to CD24. The result demonstrated that IMM47 binding to CD24 is independent of N-glycosylation modifications. (E) Analysis of cross binding activity between IMM47 and different species’ CD24 by ELISA. The result showed that IMM47 bind to CD24 protein of human and chimpanzee, and not for cyno monkey, rat and pig. (F) Binding activity of IMM47 to human RBCs or RBCs of mouse expressing human CD24, measured by FACS. The result showed that IMM47 did not bind to human RBCs but bind to RBCs of hCD24 Tg mouse.