Figure 1.
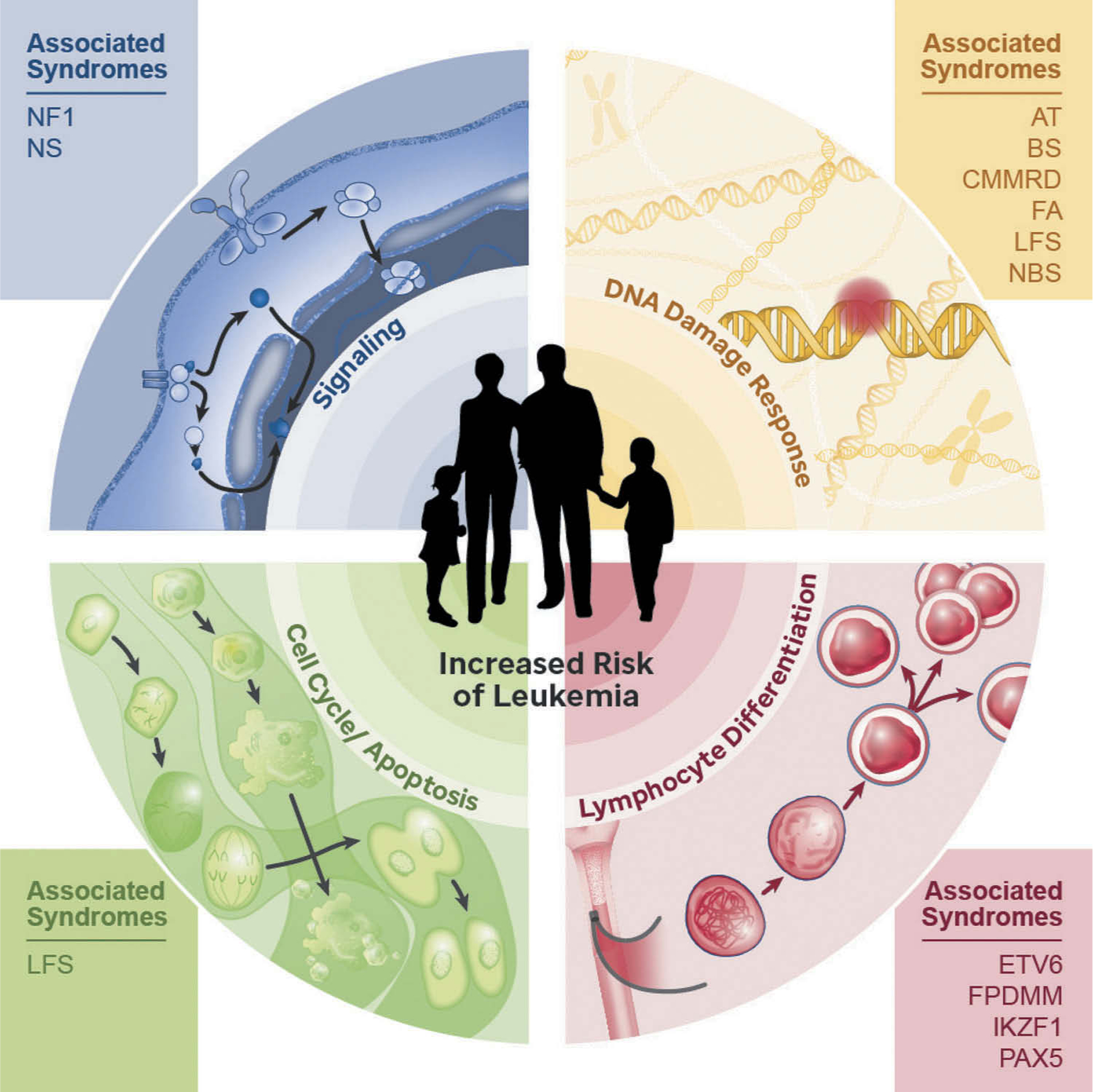
Predisposition to pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia results from germline variants affecting genes that encode proteins involved in critical pathways such as cellular signaling, DNA damage response, cell cycle, cell death, and lymphocyte differentiation. AT, Ataxia Telangiectasia; BS, Bloom syndrome; CMMRD, Constitutional mismatch repair deficiency; ETV6, ETV6-associated predisposition; FA, Fanconi anemia; FPDMM, Familial platelet disorder with predisposition to myeloid malignancy; IKZF1, IKZF1-associated predisposition to B-ALL; LFS, Li-Fraumeni syndrome; NBS, Nijmegen breakage syndrome; NF1, Neurofibromatosis type 1; NS, Noonan syndrome; PAX5, PAX5-associated leukemia predisposition.
