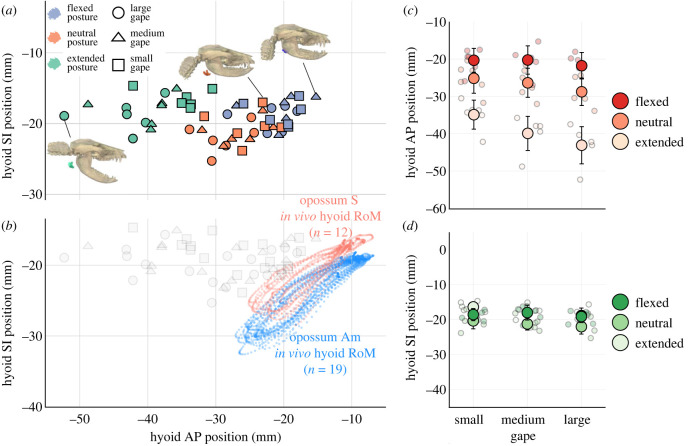
Figure 2.
Head flexion shifts static hyoid position rostrally relative to the cranium in Didelphis. Rostral shift in hyoid position is comparable with in vivo hyoid protraction magnitude during swallowing. (a) shows static hyoid position across posture-gape combinations in the horizontal (anteroposterior, AP) and vertical (superoinferior, SI) axes. Three-dimensional visualizations represent extended posture with large gape (left), neutral posture with small gape (middle), and flexed posture with medium gape (right). (b) shows in vivo hyoid range of motion (RoM) along the AP and SI axes during swallowing cycles, plotted alongside static measurements at different posture-gape combinations in grey. (c,d) show mean hyoid position at each posture-gape combination overlaid above individual measurements in each anatomical axes. Error bars are standard deviations.