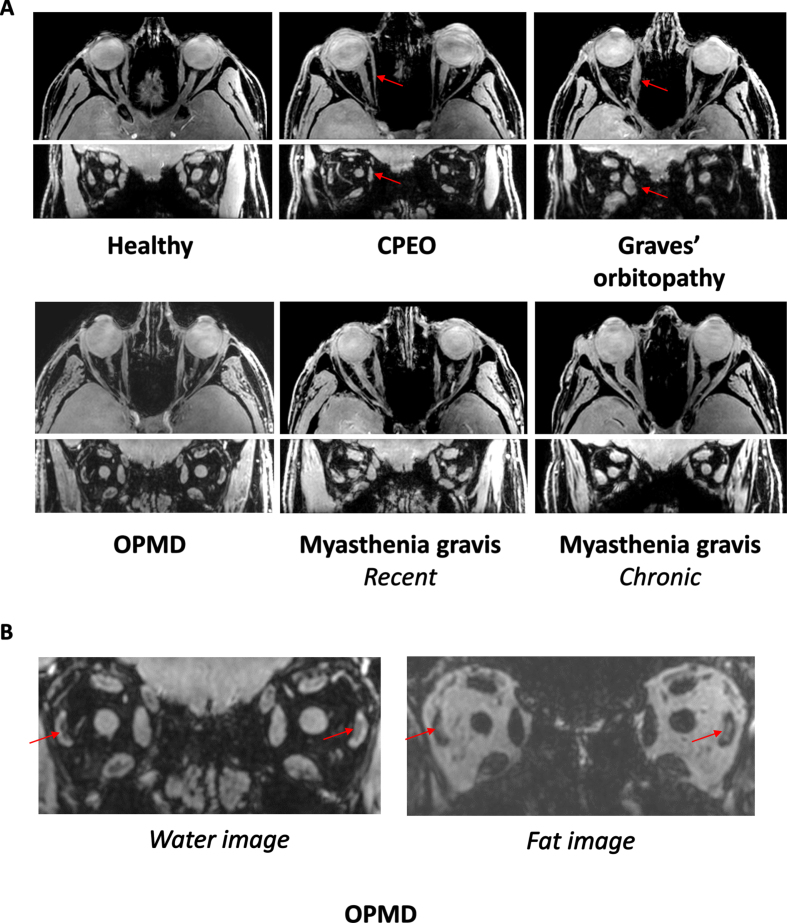
Fig. 1.
A. MRI scans from the orbit showing the extra-ocular muscles in a healthy control, a chronic progressive external orbitopathy (CPEO) patient, a Graves’ orbitopathy patient, an oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy (OPMD) patient, a recent myasthenia gravis patient and a chronic myasthenia gravis patient. The axial and coronal water images are shown from a chemical shift based water-fat separation gradient echo scan, a technique to separately image and quantify water and fat. The red arrows indicate the atrophic medial rectus muscle in the CPEO patient and the swollen medial rectus muscle in the Graves’ orbitopathy patient. B. Example of fat replacement of the lateral rectus muscles in an OPMD patient as depicted by the red arrows. On the left the coronal water image and on the right the coronal fat image are shown.