Figure 3.
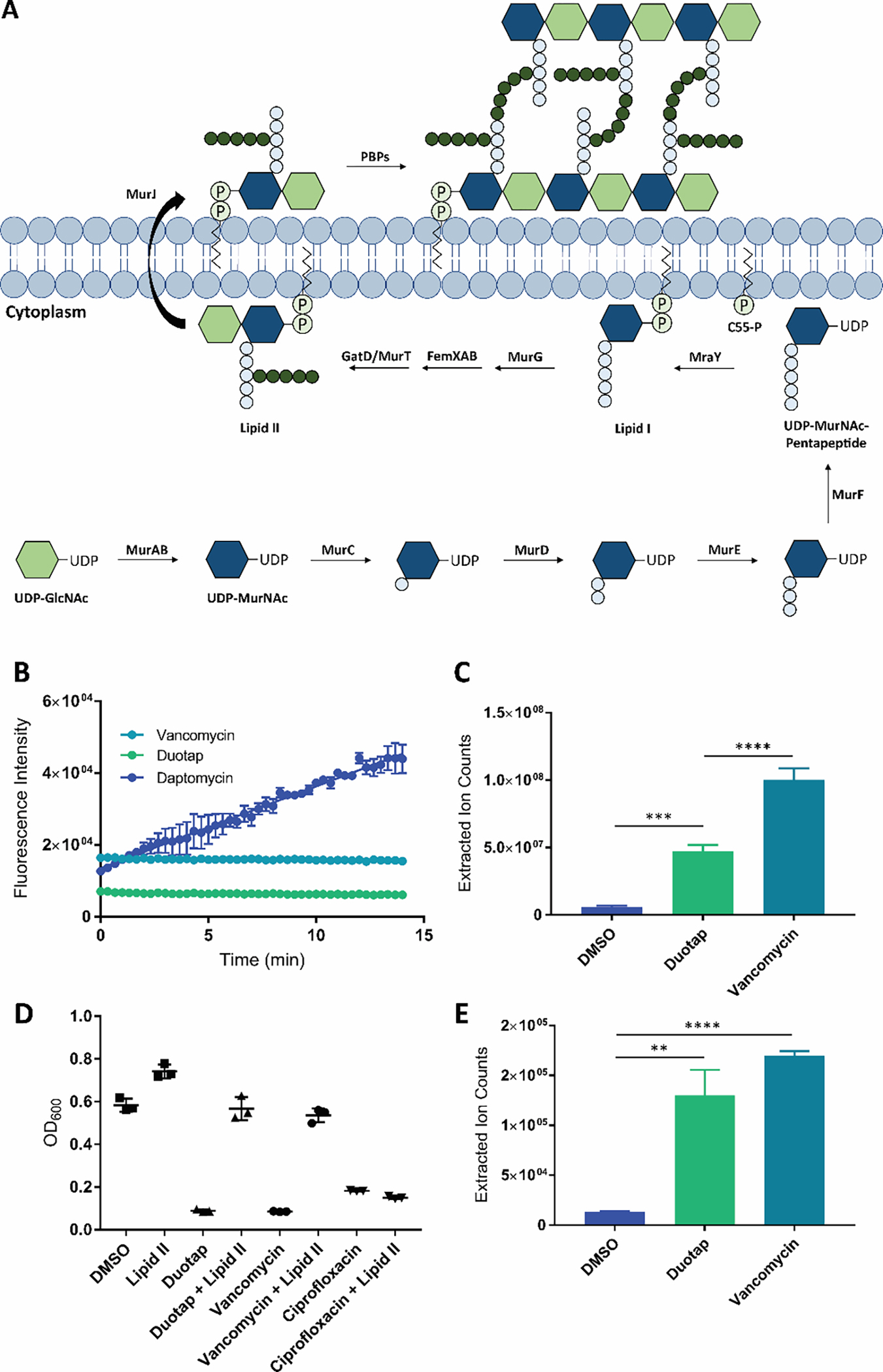
(A) MRSA cell wall biosynthesis. The intermediate lipid II is synthesized, flipped outside of the cell membrane, and polymerized into peptidoglycan by the penicillin binding proteins (PBPs).18, 19 (B) SYTOX Green fluorescence assay for antibiotic-induced bacterial membrane permeability. Vancomycin was used as a negative control, and daptomycin was used as a positive control. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean across three biological replicates. (C) Accumulation of the cell wall precursor UDP-MurNAc-pentapeptide in MRSA treated with duotap-520 compared to cells treated with vehicle DMSO. Vancomycin was used as a positive control. The UDP-MurNAc-pentapeptide was identified by mass spectrometry, with an [M+H]+ of 1150.3590. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three biological replicates. (D) Supplementation of lipid II in the growth medium can restore growth of MRSA exposed to duotap-520 and vancomycin (known to bind lipid II) to antibiotic-free levels. Lipid II cannot rescue bacteria grown in the presence of negative control ciprofloxacin (a DNA gyrase inhibitor). Data from three biological replicates are shown. (E) Accumulation of lipid II in MRSA treated with duotap-520 compared to cells treated with vehicle DMSO. Vancomycin was used as a positive control. Lipid II was boiled to remove the lipid tail, and de-lipidated lipid II was quantified by mass spectrometry, with an [M+H]+ of 1331.5362. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three biological replicates.
