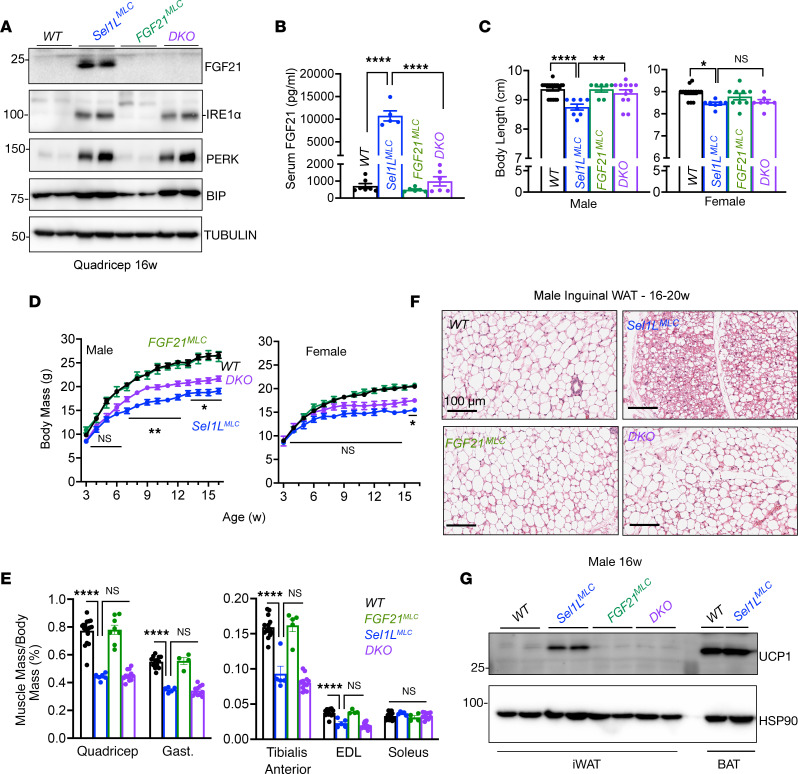
Figure 8. FGF21 links SEL1L-HRD1 ERAD in skeletal muscle to systemic metabolic regulation.
(A) Representative Western blot of ER homeostasis proteins and FGF21 in WT, Sel1LMLC (SKO), FGF21MLC (FKO), and Sel1L/Fgf21 double knockout (DKO) mice (n = 4 mice per genotype). (B) Serum measurement of FGF21 from male and female mice at 16–20 weeks old (n = 5–7 per genotype). (C) Body length of 16-week-old mice (n = 7–20 for males, n = 7–14 for females). (D) Weekly body mass of male and female mice (n = 6–44 per genotype/time point for males, n = 5–45 per genotype/time point for females). Statistical comparison made between Sel1LMLC and DKO mice. (E) Muscle mass–to–body mass ratios in male mice (n = 4–18 per genotype). Comparisons were made between indicated groups. FKO muscle was not statistically different from WT. (F) Representative H&E-stained images of inguinal white adipose tissue (n = 3 mice per genotype). (G) Representative Western blot of UCP1 in WT, Sel1LMLC, FGF21MLC, and DKO mice (n = 4 mice per genotype). Data presented as mean ± SEM. NS, P > 0.05; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ****P < 0.0001 determined by 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple-comparison test (B, C, and E) or mixed-effects analysis (repeated-measure ANOVA) with Tukey’s multiple-comparison test (D).