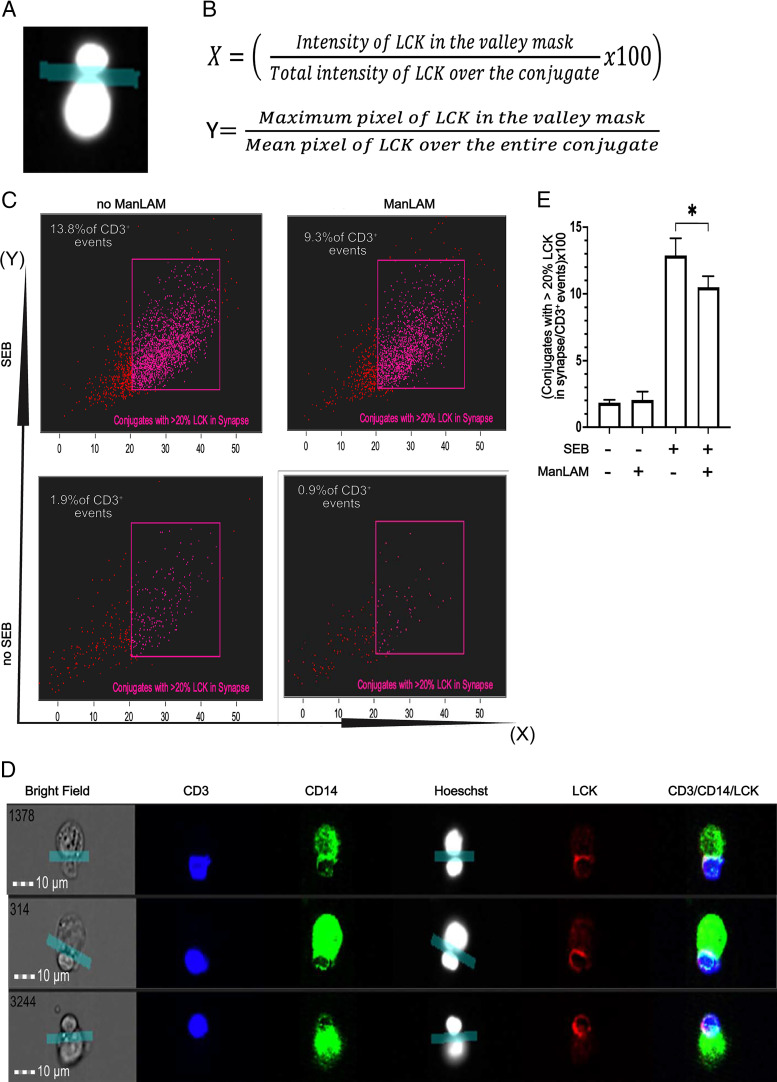
FIGURE 5.
Exposure to ManLAM reduces the percentage of conjugates with at least 20% of total LCK in the IS of CD4+ T cells and THP-1 cells. Human CD4+ T cells were incubated with or without ManLAM (40 µg/ml) for 1 h, and THP-1 cells were treated with SEB (5 µg/ml), then cocultured, stained for CD3, CD14, and LCK, and acquired as described in Fig. 4. (A) An IS was defined by applying the valley mask feature of IDEAS software to the interface of the Hoechst dye–stained nuclei of CD3+ and CD14+ cells as shown in representative image from one of four experiments from two donors. (B) Two parameters were used to measure LCK translocation to the IS: (1) redistribution of LCK (as % of total cellular LCK) to the IS in the valley mask, and (2) the ratio of maximum brightness (maximum pixel) of LCK in the IS to the mean brightness (mean pixel) of LCK over the entire cell. (C) IFC dot plots for conjugates with at least 20% of LCK in the IS as a percentage of total CD3+ events gated when the parameters described in (B) were applied. Representative dot plots of one experiment of four from two donors are shown. (D) IFC images showing translocation of LCK to the IS. Representative images of one experiment of four from two donors are shown. (E) Summary data from four experiments from two independent donors of CD4+ T cells (mean ± SEM, paired t test, *p ≤ 0.05).