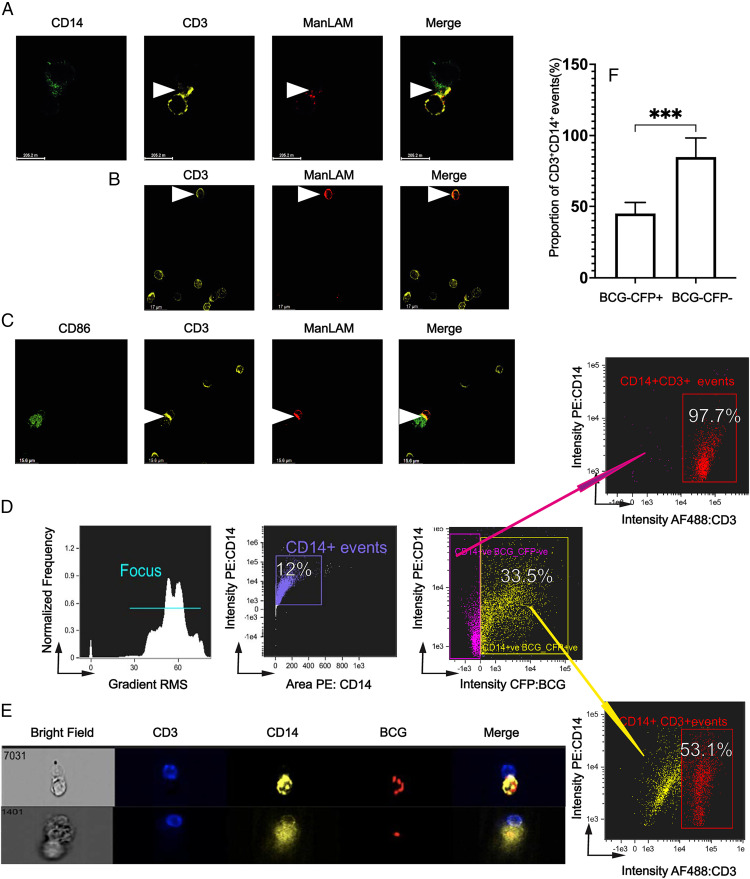
FIGURE 6.
ManLAM is transferred from BCG-infected monocytes to CD4+ T cells, localizes to the IS, and reduces conjugate formation of CD4+ T cells with infected monocytes. (A) ManLAM localizes to the IS as determined by confocal microscopy. Purified human CD4+ T cells were incubated with ManLAM (40 µg/ml) for 1 h and cocultured at 1:1 with THP-1 cells loaded with SEB (5 µg/ml) for 30 min. Cocultured cells were layered on glass slides and incubated for 15 min and then stained for CD3, CD14, and ManLAM for 3 h followed by respective secondary Abs for 1 h. Slides were imaged under 60× oil immersion. Representative confocal microscopy images from one of two experiments from two donors are shown with ManLAM localizing to the synapse (white arrow). (B) ManLAM is transferred to CD4+ T cells by BCG-infected monocytes. Primary monocytes were infected with BCG for 48 h at MOI 5:1 before addition of autologous CD4+ T cells. CD4+ T cells and BCG-infected monocytes were cocultured for 72 h. Cocultures were then layered on glass slides and incubated for 15 min and then stained with rabbit anti-CD3 and human anti-LAM (L1AM04) for 3 h followed by the respective secondary Abs for 1 h. Slides were imaged under 60× oil immersion. Representative confocal microscopy images from one of three experiments from three donors showing ManLAM staining of CD4+ T cells (white arrow) are shown. (C) ManLAM localizes to the IS when CD4+ T cells are cocultured with BCG-infected monocytes. Primary monocytes were infected with BCG at MOI 5:1 for 48 h and cocultured with autologous CD4+ T cells as in (B). Afterward, SEB was added for 1 h. Cocultures were layered on glass slides and incubated for 15 min and then stained with rabbit anti-CD3, mouse anti-CD86, and human anti-LAM (L1AM04) for 3 h followed by the respective secondary Abs for 1 h. Slides were imaged under 60× oil immersion. Representative confocal microscopy images from one of three experiments from three donors showing ManLAM localizing to the IS of CD4+ T cells cocultured with BCG-infected monocytes (white arrow) are shown. (D–F) BCG infection reduces CD4+ T cell–monocyte conjugate formation. Primary monocytes were infected with CFP-BCG for 48 h at MOI 1:1 before addition of autologous CD4+ T cells. CD4+ T cells and BCG-infected monocytes were cocultured for 72 h. Then SEB was added for 1 h. Cocultured cells were stained with AF488-conjugated anti-CD3 and PE-conjugated anti-CD14 mAbs and acquired for IFC on ImageStream imaging flow cytometer. (D) IFC gating strategy in which two populations of CD14+ events were defined: CD14+BCG/CFP+ (infected) and CD14+BCG/CFP− (noninfected). Representative IFC dot plots from one experiment of three from three donors are shown. (E) Images of CD4+ T cell–monocyte conjugates with infected monocytes (CD3+CD14+BCG/CFP+). Representative images from one experiment of three from three donors are shown. (F) Summary percentages of three experiments from three donors showing BCG-infected versus BCG-uninfected monocytes that form conjugates with CD4+ T cells (***p ≤ 0.001).