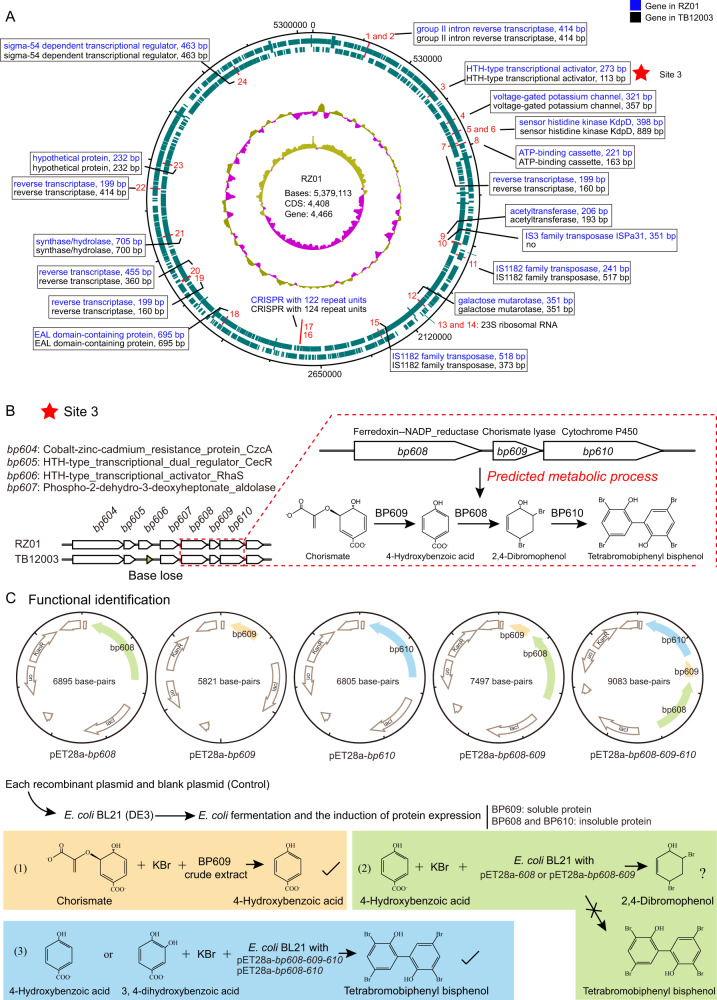
Fig. 2. Identification and functional verification of key genes in the synthesis of 4-BP in Microbulbifer sp. RZ01.
A Comparing the genomes of Microbulbifer sp. RZ01 and TB12003 and their differential loci. From the outside-in: the first and second circles indicate predicted coding regions on the plus and minus strands, respectively; the third and fourth circles represent percent G + C content and GC skew plot, respectively. The distinct sites between RZ01 and TB12003 are marked labeled with numbers 1–24. B The predicted gene cluster, bp608-610, responsible for 4-BP synthesis in Microbulbifer sp. RZ01. A base loss at site 3 resulted in the absence of an HTH-type transcriptional activator in TB12003. Site 3 was located upstream of a potential gene cluster including four genes identified as encoding phospho-2-dehydro-3-deoxyheptonate aldolase (BP607), ferredoxin-NADP reductase (BP608), 4-hydroxybenzoate synthetase (BP609), and cytochrome P450 (BP610). The bp608, bp609 and bp610 genes were predicted to be involved in the conversion of chorismate to 4-BP, based on previous research on the biosynthesis of polybrominated aromatic organic compounds (Agarwal et al. 2014). C Heterologous expression and functional validation of the bp608, bp609 and bp610 genes, which are responsible for the synthesis of 4-BP. Protein BP609 could convert the chorismate to 4-hydroxybenzoic acid in the presence of bromide ions. The function of BP608 for the conversion of 4-hydroxybenzoic acid to 2, 4-dibromophenol was not determined, however, the co-expression of BP608 and BP610 could convert 4-hydroxybenzoic acid or 3, 4-dihydroxybenzoic acid to 4-BP in the presence of bromide ions.