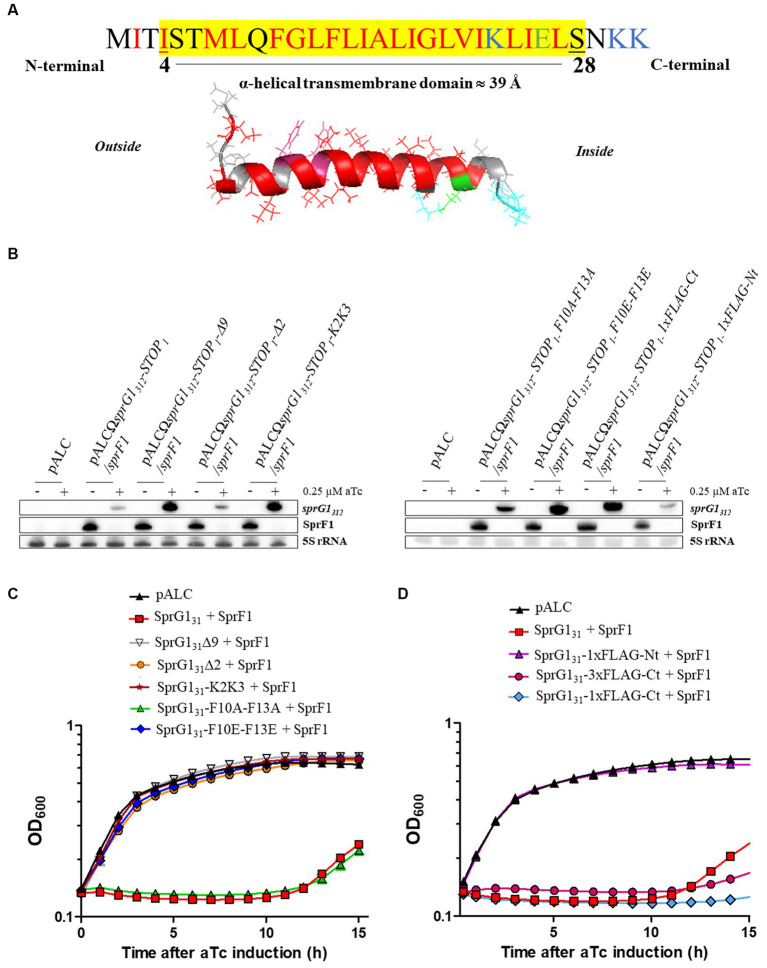
Figure 2.
Toxicity of SprG131 mutants in Staphylococcus aureus. (A) Schematic representations of the SprG131 toxin with the α-helical domain ranging from I4 to S28. The putative transmembrane domain, highlighted in yellow, is predicted using the DeepTMHMM algorithm along with the orientation of the computed in silico model of α-helix from the inside to the outside of the bacterial membrane (Hallgren et al., 2022). Hydrophobic amino acids are shown in red, negatively charged amino acids in green and positively charged amino acids in blue. (B,C) S. aureus N315ΔsprG1/sprF1 strains carrying pALC, pALCΩsprG1312-STOP1/sprF1 (SprG131 + SprF1), pALCΩsprG1312-STOP1-Δ9/sprF1 (SprG131Δ9 + SprF1), pALCΩsprG1312-STOP1-Δ2/sprF1 (SprG131Δ2 + SprF1), pALCΩsprG1312-STOP1-K2K3/sprF1 (SprG131-K2K3 + SprF1), pALCΩsprG1312-STOP1-F10A-F13A/sprF1 (SprG131-F10A-F13A + SprF1), pALCΩsprG1312-STOP1-F10E-F13E/sprF1 (SprG131-F10E-F13E + SprF1), pALCΩsprG1312-STOP1 1xFLAG-Nt/sprF1 (SprG131-1xFLAG-Nt + SprF1), pALCΩsprG1312-STOP1 1xFLAG-Ct/sprF1 (SprG131-1xFLAG-Ct + SprF1) and pALCΩsprG1312-3xFLAG-Ct-STOP1/sprF1 (SprG131-3xFLAG-Ct + SprF1) were cultivated in MH medium until the exponential growth phase and incubated in the absence (−) or presence (+) of 0.25 μM aTc. (B) After RNA extraction, northern blot analysis was done on sprG1312, sprG1312 mutants and SprF1 expression with 5S rRNA used as the loading control. (C,D) Growth kinetics of S. aureus strains after aTc induction. Error bars show the means and standard deviations of three biological replicates (n = 3).