Figure 2.
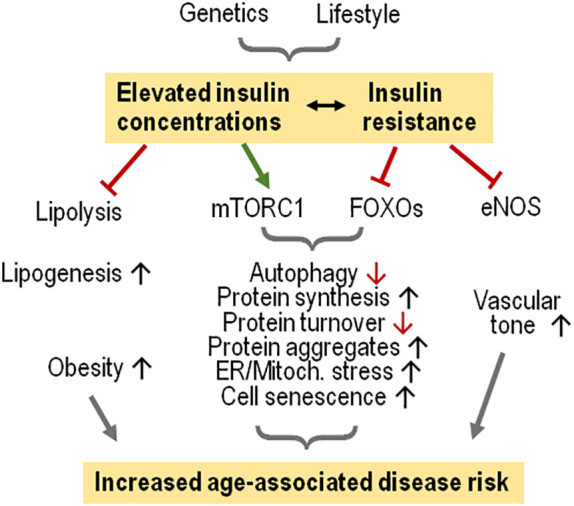
Elevated insulin levels and insulin resistance favor age-associated diseases in humans. Modest increases of insulin concentrations suffice to suppress lipolysis and support lipogenesis, promoting obesity. Hyperinsulinemia combined with insulin resistance cause activation of mTORC1 which in the context of less FOXO activation favors cell stress because of increased protein synthesis, eventually causing cell senescence. Insulin resistance impairs endothelial NO synthase (eNOS) activity, limiting vascular relaxation.
