FIGURE 1.
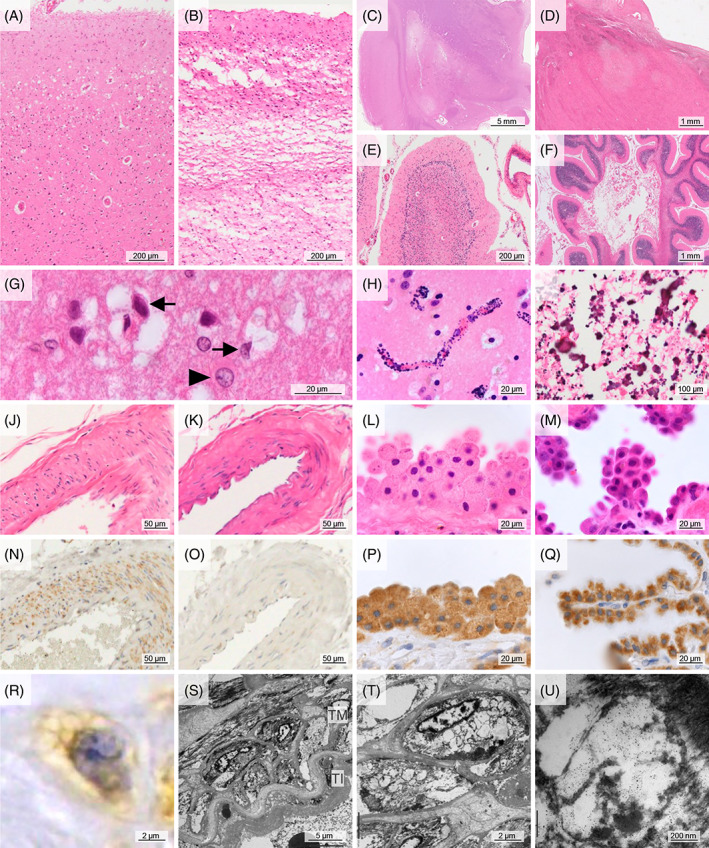
Common neuropathological findings of cases with the m.3243A>G mutation. (A, G) Superficial vacuolation of the cerebral cortex in case M5. A high magnification view demonstrated type II astrocytes (arrowhead) and various sizes of vacuolations surrounding neurons (arrows). (B) Laminar necrosis of the cerebral cortex in case M3. (C, D) Necrotic lesions of the basal ganglia in case M1 (C) and thalamus in case M4 (D). (E) Ischemic lesion of the cerebellum in case M4, showing loss of granule cells and Purkinje cells with Bergmann gliosis. (F) Necrosis of the cerebellum in case M4. (H) Capillary mineralization in the putamen of case M3. (I) Coarse mineralization in the globus pallidus of case M3. (J, N, R) Mitochondrial vasculopathy showing swollen smooth muscle cells of the tunica media with small cytoplasmic vacuolations and mitochondria immunoreactivity in case M4. (K, O) Normal artery in case C1. (L, P) Swollen epithelial cells of the choroid plexus in case M4. (M, Q) Normal epithelial cells of the choroid plexus in case C1. (S–U) Electron microscopic images. Smooth muscle cells of the tunica media had many cytoplasmic vacuolations, presumably compatible with the ballooned mitochondria in case M1. (A–M): HE staining; (N‐Q): immunohistochemistry against mitochondria. Bar: 5 mm for (C), 1 mm for (D, F), 200 μm for (A, B, E), 100 μm for (I), 50 μm for (J, K, N, O), 20 μm for (G, H, L, M, P, Q), 5 μm for (S), 2 μm for (R, T), and 200 nm for (U). TI, tunica intima; TM, tunica media.
