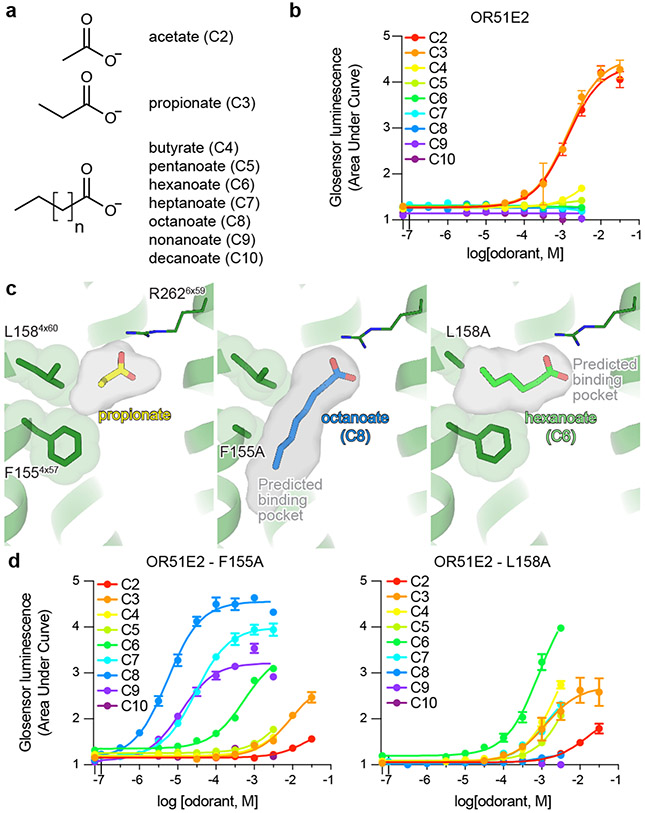
Figure 3. Tuning OR51E2 odorant selectivity.
a,b) OR51E2 responds selectively to the short chain fatty acids acetate and propionate as measured by a cAMP production assay. c) Docked poses of octanoate (C8) and hexanoate (C6) are shown in the predicted binding cavities of homology modeled OR51E2 mutants F1554x57A and L1584x60A. Binding pocket cavities are shown as gray surface. Replacement of F1554x57 and L1584x60 with alanine is predicted to yield a binding pocket with increased volume capable of accommodating longer chain fatty acids. d) The F1554x57A and L1584x60A mutations in OR51E2 lead to increased sensitivity to long chain fatty acids. Conversely, the potency for acetate and propionate is reduced for these two mutants. Data points in b and d are mean ± standard deviation from n = 4 experiments.