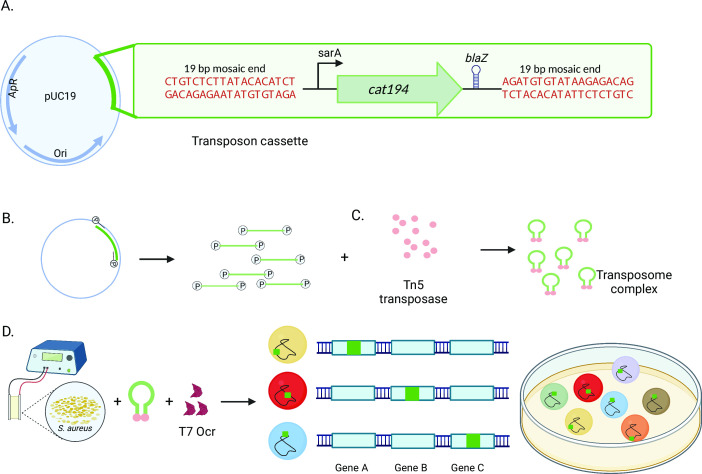
Fig 1.
Transposon mutant generation in S. aureus. (A) The transposon vector is built into a pUC19 backbone and integrates a constitutively expressed chloramphenicol antibiotic resistance marker (cat194) with a bidirectionally active transcriptional terminator. (B) Transposon is amplified using phosphorylated primers and (C) Combined with Tn5 transposase in vitro to generate stable transposome complexes. (D) Transposomes are electroporated into S. aureus with an inhibitor of the type one restriction system (Ocr), and transformants are selected for antibiotic resistance on solid media (E) to yield transposon mutant libraries.