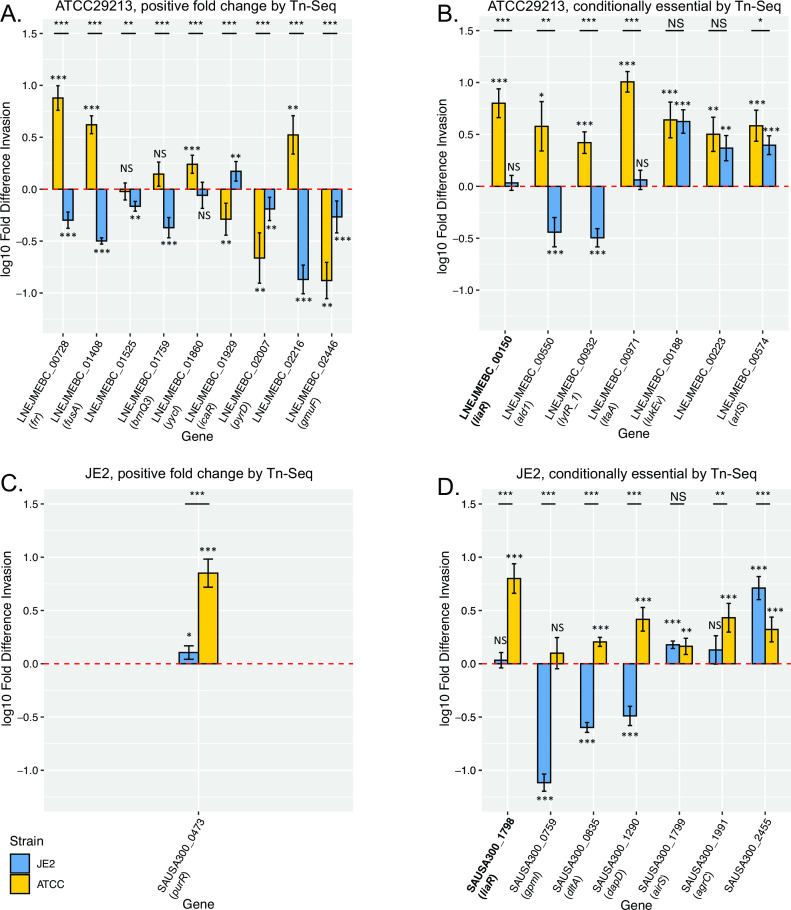
Fig 4.
Intracellular invasion phenotypes of isogenic CRISPRi knockdowns. Results are shown for the knockdown of candidate genes from Tn-Seq analysis of post-macrophage invasion mutant pools that were identified as significant and showing consistent effects relative to both the initial transposon mutant library pool and the outgrowth control. Panels indicate genes identified by Tn-Seq as: (A) ATCC29213 genes with positive fold change in abundance, (B) conditionally essential ATCC29213 genes, (C) JE2 genes with positive fold change in abundance, and (D) conditionally essential JE2 genes. Y-axes indicate the fold difference in THP-1 derived macrophage invasion for isogenic CRISPRi knockdowns in both S. aureus strains relative to invasion activity of the matched parental strain carrying a silencing vector targeted to an irrelevant biological target (GFP), represented by a dashed line (red, at 0). Error bars indicate SEM. Measured values that are significantly different (by 2-tailed t test) are indicated by asterisks: *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001, either against the parental strain (displayed above each bar plot) or for the indicated comparisons between strains (black lines). NS, not significant. Common gene names, where applicable, are indicated in parentheses below each gene ID. liaR, relevant to both strains, is in bold.