Abstract
The hydroxylation of the indole-type alkaloids, yohimbine, α-yohimbine, β-yohimbine, and corynanthine, was achieved with several genera of higher fungi and species of Streptomyces. Microorganisms were found which monohydroxylated these compounds in three different positions. The site of hydroxylation was strain-specific for two strains of Cunninghamella echinulata and C. bainieri.
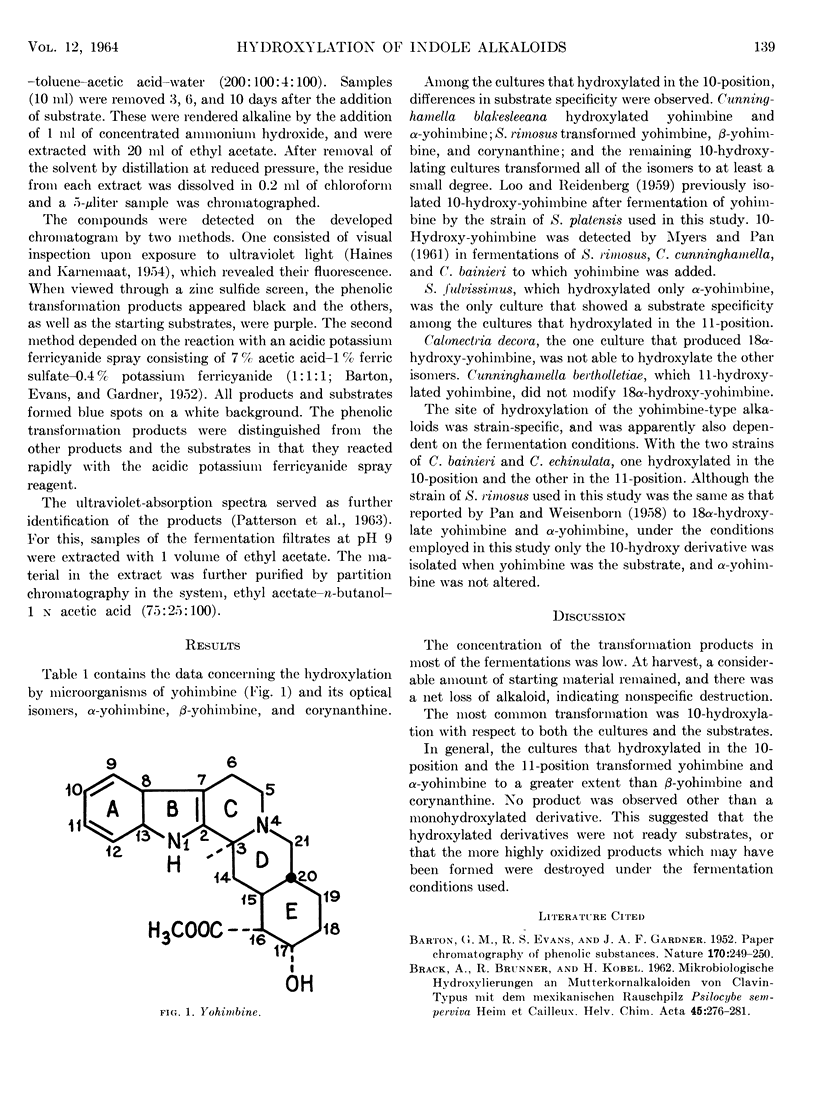
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- HAINES W. J., KARNEMAAT J. N. Chromatographic separation of the steroids of the adrenal gland. Methods Biochem Anal. 1954;1:171–204. doi: 10.1002/9780470110171.ch7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYERS E., PAN S. C. Microbial transformation of Rauwolfia alkaloids. II. 10-Hydroxyyohimbine. J Bacteriol. 1961 Mar;81:504–505. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.3.504-505.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIEMER H., BUCHERER H., KOHLER A. [On the decomposition of atropine by Corynebacterium belladonnae]. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1959;317:238–242. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1959.317.1.238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATTERSON E. L., ANDRES W. W., KRAUSE E. F., HARTMAN R. E., MITSCHER L. A. THE MICROBIOLOGICAL TRANSFORMATION OF SOME YOHIMBINE-TYPE ALKALOIDS. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Oct;103:117–123. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90017-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


