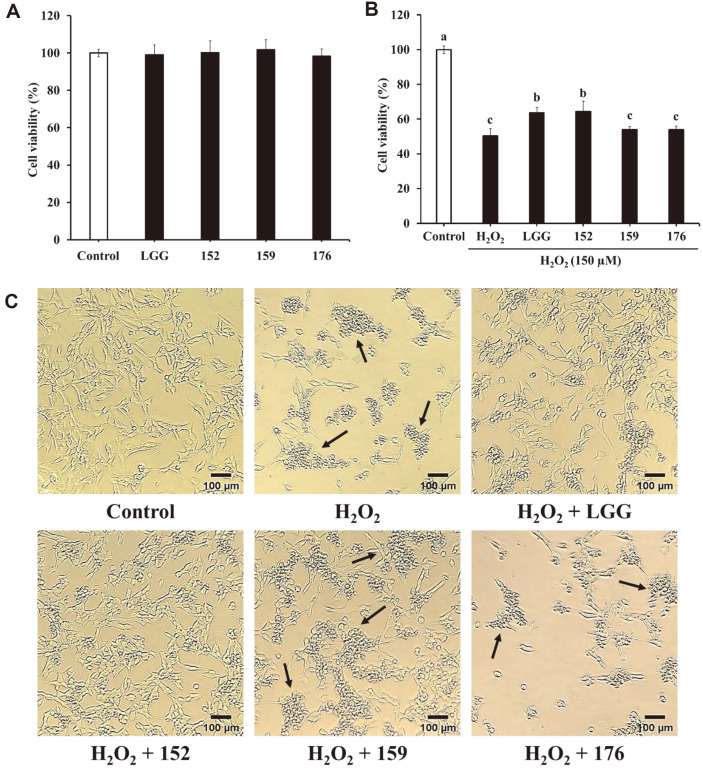
Fig. 1. Neuroprotective effects of heat-killed LAB–CM on H2O2-induced toxicity in SH-SY5Y cells.
(A) Effect of LAB–CM on cell viability in SH-SY5Y cells. (B) Effect of LAB–CM on cell viability of H2O2-treated SH-SY5Y cells. (C) Morphological changes in SH-SY5Y cells investigated using microscopy (magnification: 40×). Arrows indicate aggregation and shrinkage of SH-SY5Y cells. LGG, CM of heat-killed L. rhamnosus GG; 152, CM of heat-killed L. brevis KU15152; 159, CM of heat-killed L. brevis KU15159; 176, CM of heat-killed L. brevis KU15176. Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation of triplicate experiments. Different letters on the error bars represent significant differences (p < 0.05).