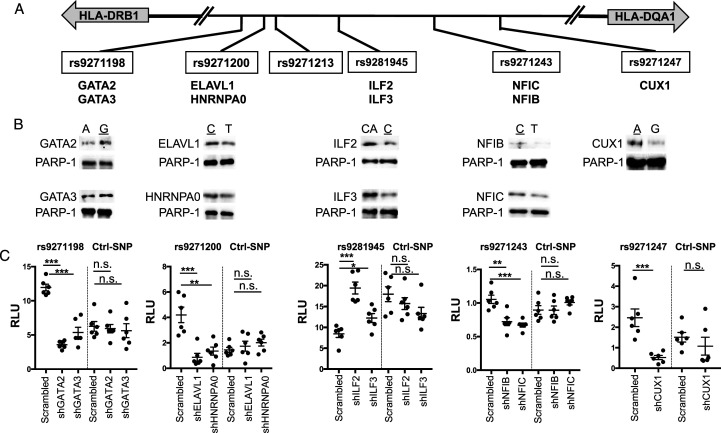
Figure 2.
Characterization of nine proteins that specifically bind to the five fSNPs at the HLA-DQA1/DRB1 locus. (A). Partial genomic arrangement showing the relative location of the 6 fSNPs in between HLA-DQA1 and HLA-DRB1 and the nine proteins identified by SDCP-MS. Risk alleles are underlined. (B). AIDP-Wb showing the allele-imbalanced binding of GATA2 and GATA3 to rs9271198; ELAVL1and HNRNPA0 to rs9271200; ILF2 and ILF3 to rs9281945; NFIB and NFIC to rs9271243; and CUX1 to rs9271247. PARP-1, a double-stranded DNA end binding protein was used as an internal loading control. Data for AIDP-Wb represents three biologically independent experiments (n = 3). (C). Luciferase reporter assay demonstrating the specific binding of these nine proteins to their corresponding fSNPs by showing altered luciferase activities when all these nine proteins were downregulated by shRNA knockdown in HMC3 cells. Ctrl: negative control with an irrelevant SNP sequence. Data for luciferase reporter assay represents 6 biologically independent repeats (n = 6). * P < .05; ** P < .001; and *** P, .0001. n.s.: not significant.