Figure 3.
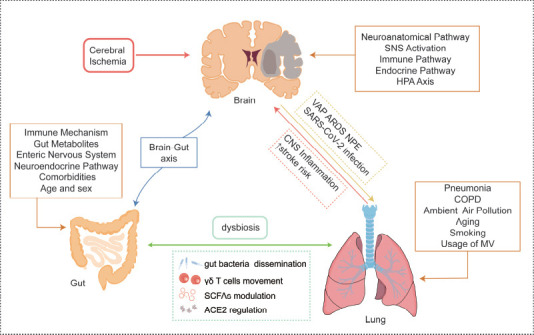
The lung-brain axis and gut-lung axis in ischemic stroke.
Ischemic stroke will cause a series of pulmonary complications though neuroanatomical and other pathways. In turn, the lung influenced by pneumonia and COPD and many other issues will in the end lead to CNS inflammation and increase the risk of stroke and poor outcomes. The above section has introduced the brain-gut axis’ different mechanisms, and the interaction between the gut and lung involves gut microbiota translocation, γδ T cells movement, and metabolite changes such as SCFAs and ACE2. Created with Adobe Illustrator 2019. ACE2: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; ARDS: acute respiratory distress syndrome; CNS: central nervous system; COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; MV: mechanical ventilation; NPE: neurogenic pulmonary edema; SCFAs; short-chain-fatty acids; VAP: ventilator-associated pneumonia.
