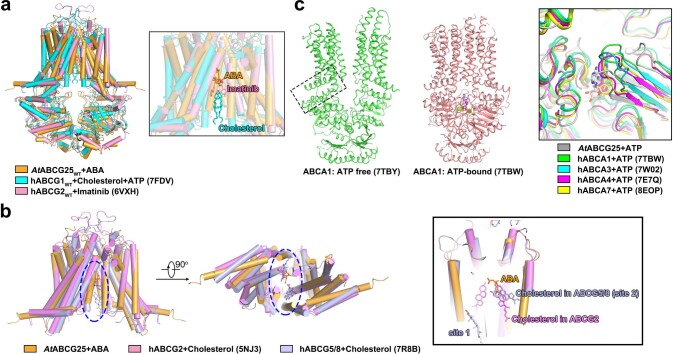
Extended Data Fig. 9. Structural comparisons between ABCG25 in Arabidopsis and human ABCs.
a, Structure alignments of ABCG25WT and hABCG1WT (PDB code: 7FDV), hABCG2WT (PDB code: 6VXH) in the substrate/inhibitor-bound state. b, Superposition of the ABA-bound ABCG25, the cholesterol-bound hABCG2 (PDB code: 5NJ3) and the cholesterol-bound hABCG5/8 (PDB code: 7R8B). c, Conserved ATP-induced conformation changes between ABCG25 and ABCAs. Shown here are the representative human cholesterol transporter ABCA1 in the ATP-free (PDB code: 7TBY) and ATP-bound (PDB code: 7TBW) state, respectively. The connecting helices are indicated by the dashed-line box. The large extracellular domain of ABCA1 is hidden. The inner panel shows structure alignments of the ATP binding site in ABCG25, hABCA1 (7TBW), hABCA3(7W0W), hABCA4 (7E7Q) and ABCA7 (8EOP) in the ATP-bound state.