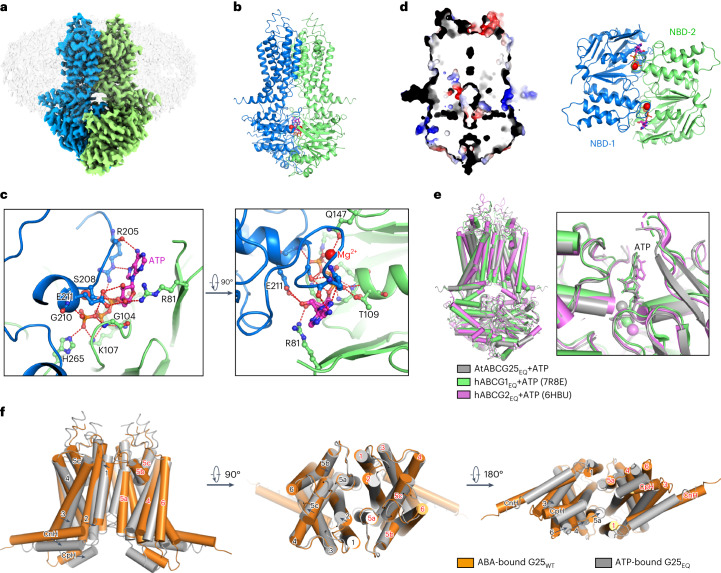
Fig. 4. Architecture of ABCG25EQ in the ATP-bound state.
a, Overview of the electron density for the ABCG25 E232Q mutant in the ATP-bound state. Densities corresponding to the ABCG25 monomers are coloured blue and green. The detergent density is shown in grey. b, Overall structure of the ATP-bound ABCG25EQ and the EM density for the ATP molecule (with nitrogen and phosphorus atoms coloured magenta and orange, respectively) and magnesium (coloured red). c, Coordination of ATP and Mg2+ by ABCG25. The ATP molecule and interacting residues are shown as sticks in the zoom-in views. Hydrogen bonds are shown as red dashed lines. d, Section view of the surface electrostatic potential of the ATP-bound ABCG25EQ (left) and a cartoon representation of the NBDs with the ATP-binding site (right). e, Structure alignments of ABCG25EQ, hABCG1EQ (PDB code: 7R8E) and hABCG2EQ (PDB code: 6HBU) in the ATP-bound state. ABCG25, hABCG1 and hABCG2 are coloured grey, green and pink, respectively. f, Comparison of the TMDs of the ABA-bound ABCG25WT (coloured orange) and the ATP-bound ABCG25EQ (coloured grey) structures.