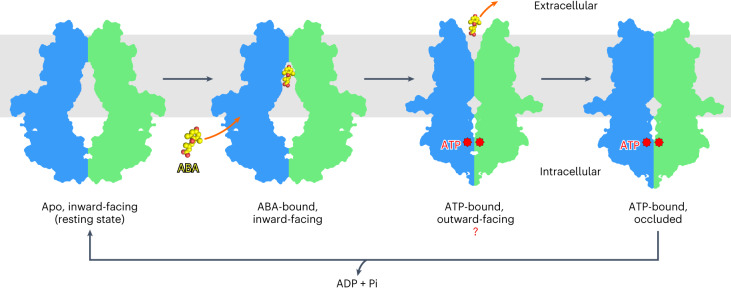
Fig. 5. A proposed model for the ABCG25-mediated ABA efflux cycle.
The ABA efflux cycle starts with the inward-facing (resting) state, in which ABCG25 is ready for ABA binding. Then, the ABA molecule binds to ABCG25 from the intracellular side. ATP binding to the NBDs of ABCG25 leads to closing of the NBDs and the conformational changes are transmitted to the TMDs through the three-helix bundles formed by CnH, CpH and E-helix. The inner parts of the TMs rotate to close the cavity and push the bound ABA to translocate along the transport path. The extracellular gate transiently opens and ABA is released to the extracellular side. ATP hydrolysis and release of ADP from NBDs reset ABCG25 to the resting state, ready for the next transport cycle. Source data.