Abstract
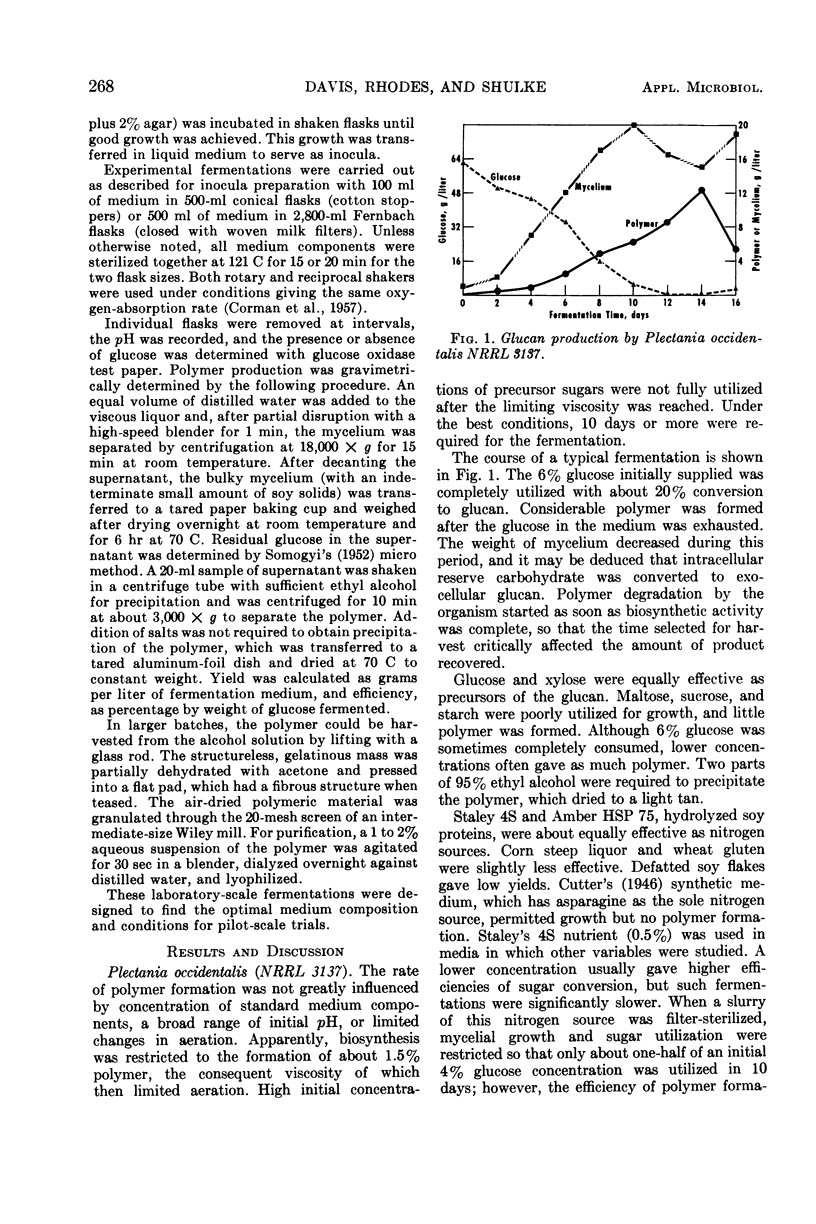
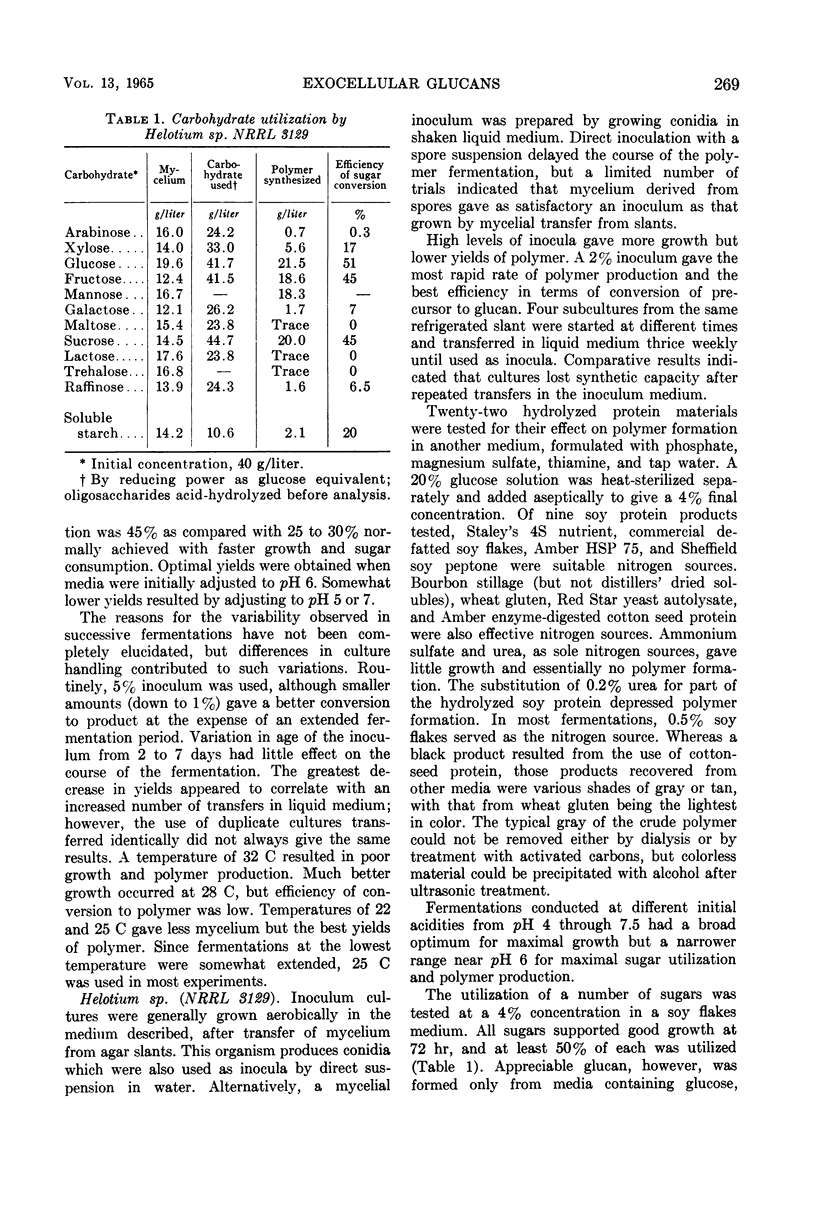
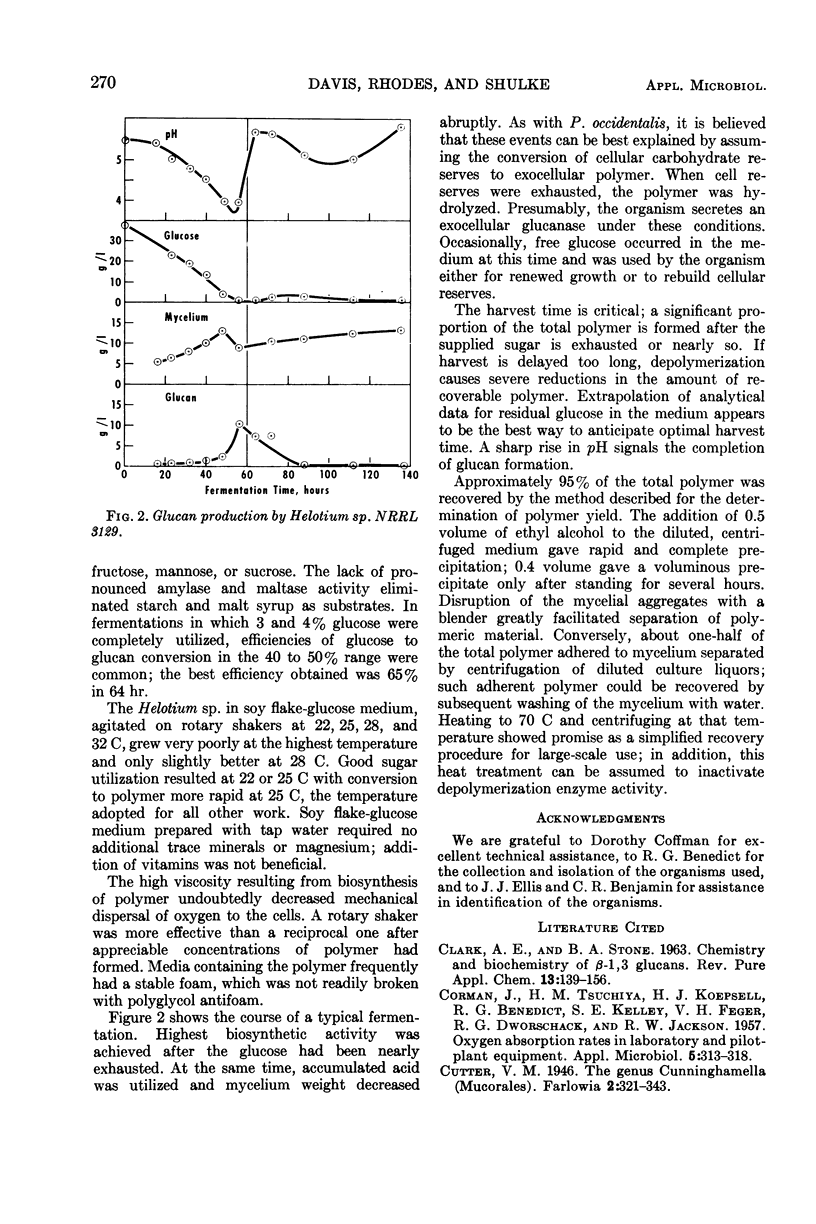
Two specimens of higher fungi produced exocellular β-1, 3-glucans when their mycelial forms were cultivated under submerged aerobic conditions. Plectania occidentalis NRRL 3137 consumed up to 6% glucose or xylose with about 30% conversion to polymer in a medium composed of hydrolyzed soy protein, salts, and thiamine. A 5% inoculum was used in a 10-day shaken fermentation. After dilution of the culture liquors and partial disruption of mycelia with a blender, solids were removed by centrifugation, and the polymer was precipitated by the admixture of 2 volumes of ethyl alcohol. A second polymer was formed in 40 to 65% yield by fermentation with Helotium sp. NRRL 3129, which in the imperfect stage would be identified as Monilia sp. It consumed up to 4% glucose, fructose, mannose, or sucrose in 60 to 72 hr. A 2% inoculum in a medium composed of commercial defatted soy flakes, phosphate, and thiamine in tap water gave a satisfactory fermentation. This polymer was precipitated by the addition of 0.5 volume of ethyl alcohol. Both organisms have a broad pH optimum on the slightly acidic side and did best at about 25 C.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CORMAN J., TSUCHIYA H. M., KOEPSELL H. J., BENEDICT R. G., KELLEY S. E., FEGER V. H., DWORSCHACK R. G., JACKSON R. W. Oxygen absorption rates in laboratory and pilot plant equipment. Appl Microbiol. 1957 Sep;5(5):313–318. doi: 10.1128/am.5.5.313-318.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REESE E. T., MANDELS M. Beta-D-1, 3 Glucanases in fungi. Can J Microbiol. 1959 Apr;5(2):173–185. doi: 10.1139/m59-022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMOGYI M. Notes on sugar determination. J Biol Chem. 1952 Mar;195(1):19–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALLEN L. L., RHODES R. A., SHULKE H. R. PHYSICAL PROPERTIES AND CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF BETA-GLUCANS FROM FLESHY FUNGI. Appl Microbiol. 1965 Mar;13:272–278. doi: 10.1128/am.13.2.272-278.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


