Figure 1.
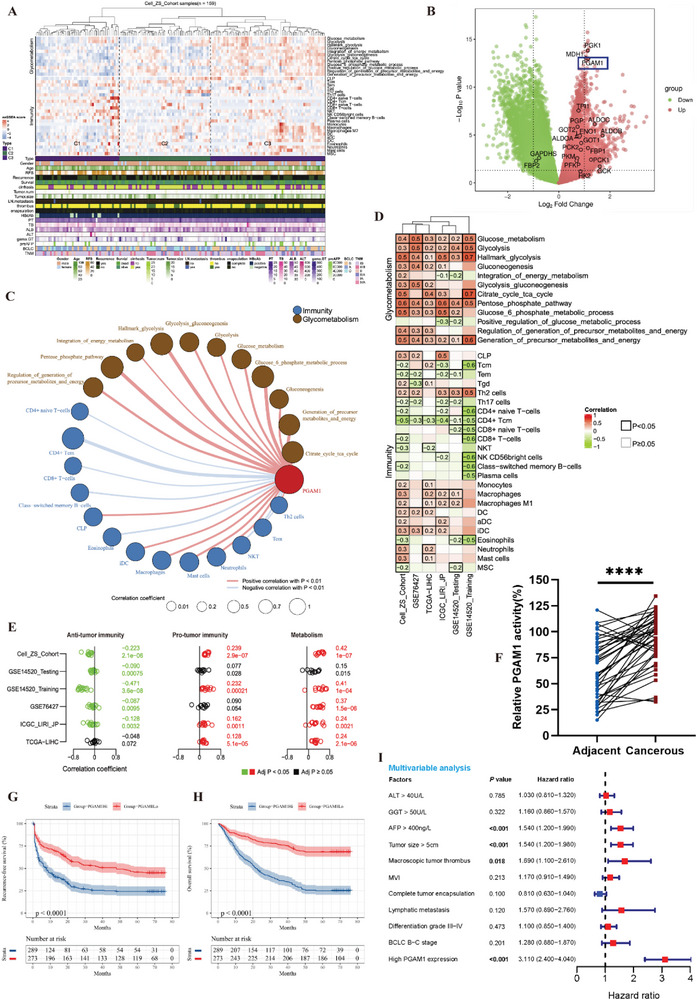
PGAM1 is a novel immunometabolic target correlated with a poor prognosis in HCC. A) Hierarchical clustering heatmap of characteristics of immune infiltration, glucose, and energy metabolism identified by ssGSEA and xCell algorithm for three clusters. C1, “low glucometabolism with anti‐tumor immune status”; C2, intermediate cluster; C3, “high glucometabolism with pro‐tumor immune status”. B) Volcano plot of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) analysis between C1 and C3. DEGs were defined as genes with adj. p < 0.05 and |log2FC| ≥1 (C3 vs C1) by using “limma” package. C) Correlation analysis network of PGAM1 expression, immune cell infiltration and glucometabolism in Cell‐ZS‐Cohort (based on xCell algorithm). D,E) Correlation heatmap (D) and forest plot (E) for PGAM1 expression, anti‐tumor immunity, pro‐tumor immunity, and metabolism in five HCC datasets (based on xCell algorithm). F) Multiple enzymes coupled assay was performed to detect the activities of PGAM1 in cancerous tissue and adjacent normal tissue in patients with HCC (n = 40, p < 0.0001, p values were obtained from paired t‐test). G,H) KaplanMeier recurrence‐free survival (RFS) (G) and overall survival (OS) (H) for HCC patients with high and low PGAM1 expression in the Zhongshan TMA cohort. I) Multivariable Cox regression analysis for clinicopathological characteristics correlated to OS of HCC patients in the Zhongshan TMA cohort.
