Figure 7.
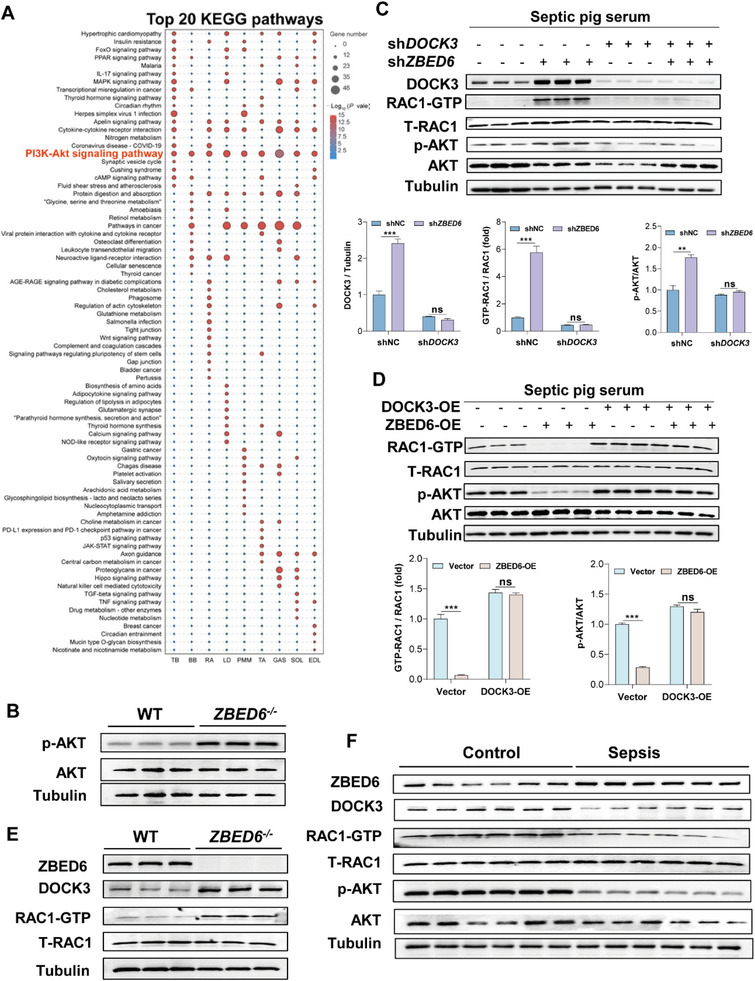
Loss of ZBED6 activates DOCK3‐mediated RAC1/AKT signaling pathway in sepsis‐induced atrophy. A) Top twenty enriched KEGG pathways of DEGs in nine depots of skeletal muscle from septic ZBED6‐deficient pigs compared with WT controls. B) Western blot images showing ZBED6 deficiency results in increased levels of p‐AKT in skeletal muscles of septic pigs. C) Western blot images showing ZBED6 depletion results in increased levels of DOCK3, active Rac1 (Rac1‐GTP), and p‐AKT in pig primary myotubes under normal or septic conditions. Pig primary myotubes infected with control lentivirus (shNC) or ZBED6 shRNA (shZBED6) lentivirus. Seventy‐two hours after infection, myotubes were treated with normal or septic pig serum for 48 h. Western blot (top) and relative quantification (bottom) of DOCK3, Rac1‐GTP, p‐AKT (S473), and AKT. D) Western blot images showing ZBED6 overexpression results in decreased levels of Rac1‐GTP and p‐AKT in pig primary myotubes under normal and septic conditions. Pig primary myotubes infected by adenovirus‐encoding ZBED6 (ZBED6‐OE) or control vector (Vector). Seventy‐two hours after infection, myotubes were treated with normal or septic pig serum for 48 h. Western blot (top) and relative quantification (bottom) of Rac1‐GTP, p‐AKT (S473), and AKT. E) Western blot images showing ZBED6 deficiency results in increased levels of DOCK3 and active Rac1 (Rac1‐GTP) in skeletal muscles of septic pigs. F) Western blot images showing increased levels of ZBED6 and decreased levels of DOCK3, Rac1‐GTPand p‐AKT in skeletal muscles of sepsis patients. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
