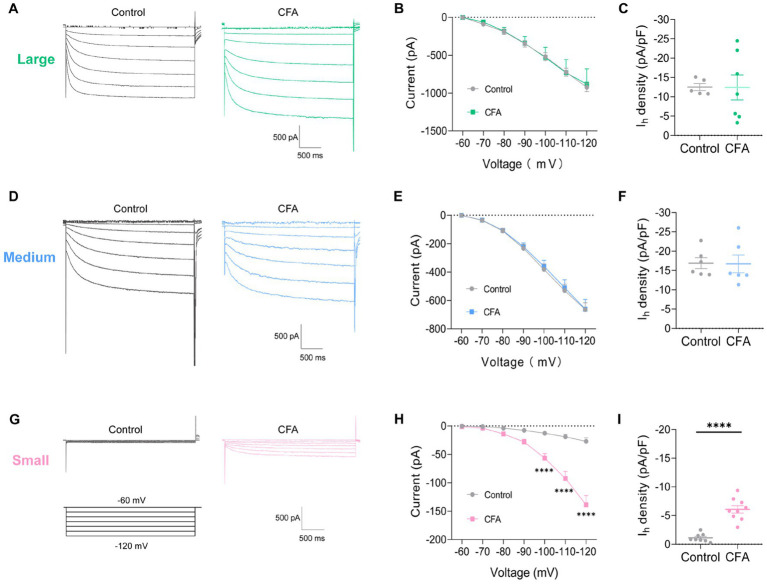
Figure 3.
CFA-induced inflammation increases Ih amplitude of small-diameter DRG neurons but not large-or medium-diameter DRG neurons. (A,D,G) Representative traces of Ih recorded in large- (A), medium- (D), and small-diameter (G) DRG neurons in response to hyperpolarizing voltage steps of −60 to −120 mV in 10 mV increments from a holding potential at −60 mV in both control and CFA-inflamed states. The voltage protocol is shown in the lower position of G. (B,E,H) Current–voltage relationship of Ih in large- (B, n = 5–7), medium- (D, n = 6), and small-diameter (F, n = 8–9) DRG neurons from control and CFA-injected mice (by two-way ANOVA, Fisher’s LSD test). (C,F,I) Ih density in large- (B, n = 5–7), medium- (D, n = 6), and small-diameter (F, n = 8–9) DRG neurons from control and CFA-injected mice (by nonparametric Mann–Whitney test), Note the Ih current densities measured at −120 mV. All data are presented as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001.