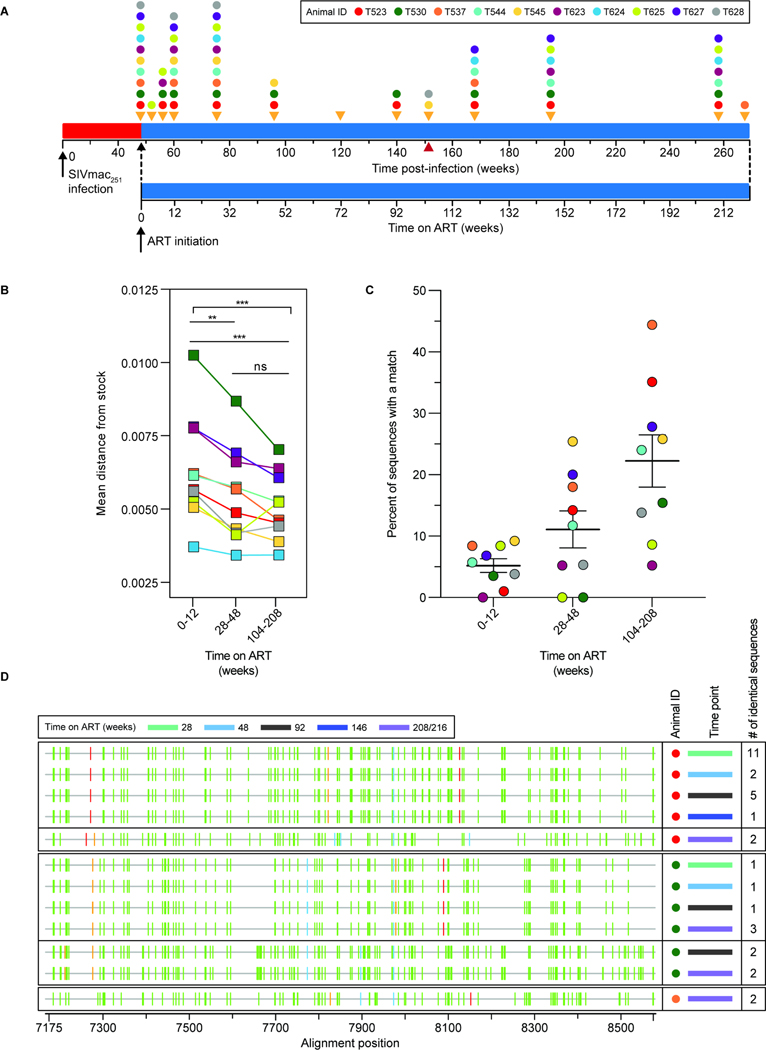
Figure 5. Analysis of env sequences from CD4+ T cell DNA during ART.
(A) Timeline for sequence analysis. Colored dots indicate sampling times for each animal. (B) Average pairwise distance from the stock57 of env sequences collected at early (weeks 0–12), intermediate (weeks 28–48) or late (weeks 104–216) time points after ART initiation. The number of sequences analyzed for each animal is listed in Table S7. Statistical significance was determined using one-way ANOVA (GraphPad Prism). (C) Percent of non-defective env sequences that exactly match another independent sequence from the same sample at early, intermediate, or late time points on ART. Sequences with hypermutation (as determined using Los Alamos National Lab’s Hypermut Program99), or deletions were excluded from this analysis. Animal T624 was excluded due to a high frequency of identical sequences at all time points, reflecting early control of replication (Fig. 1B, Fig. S13). (D) Highlighter plots of identical hypermutated env sequences from 3 animals. The animal (colored dot, see key in panel A), time point (colored bar), and the number of times an identical sequence was recovered from a given sample are indicated. Vertical bars indicate a nucleotide difference from the consensus of the stock57. The color of the bar represents the mutant nucleotide (red – thymine, blue – cytosine, orange – guanine, green – adenine). Alignment numbering corresponds to nucleotide positions based on the SIVmac239 reference (accession no: M33262.1).