Fig. 4 |. Biophysical characterization and overall architecture of the TnsC•ATP heptamer.
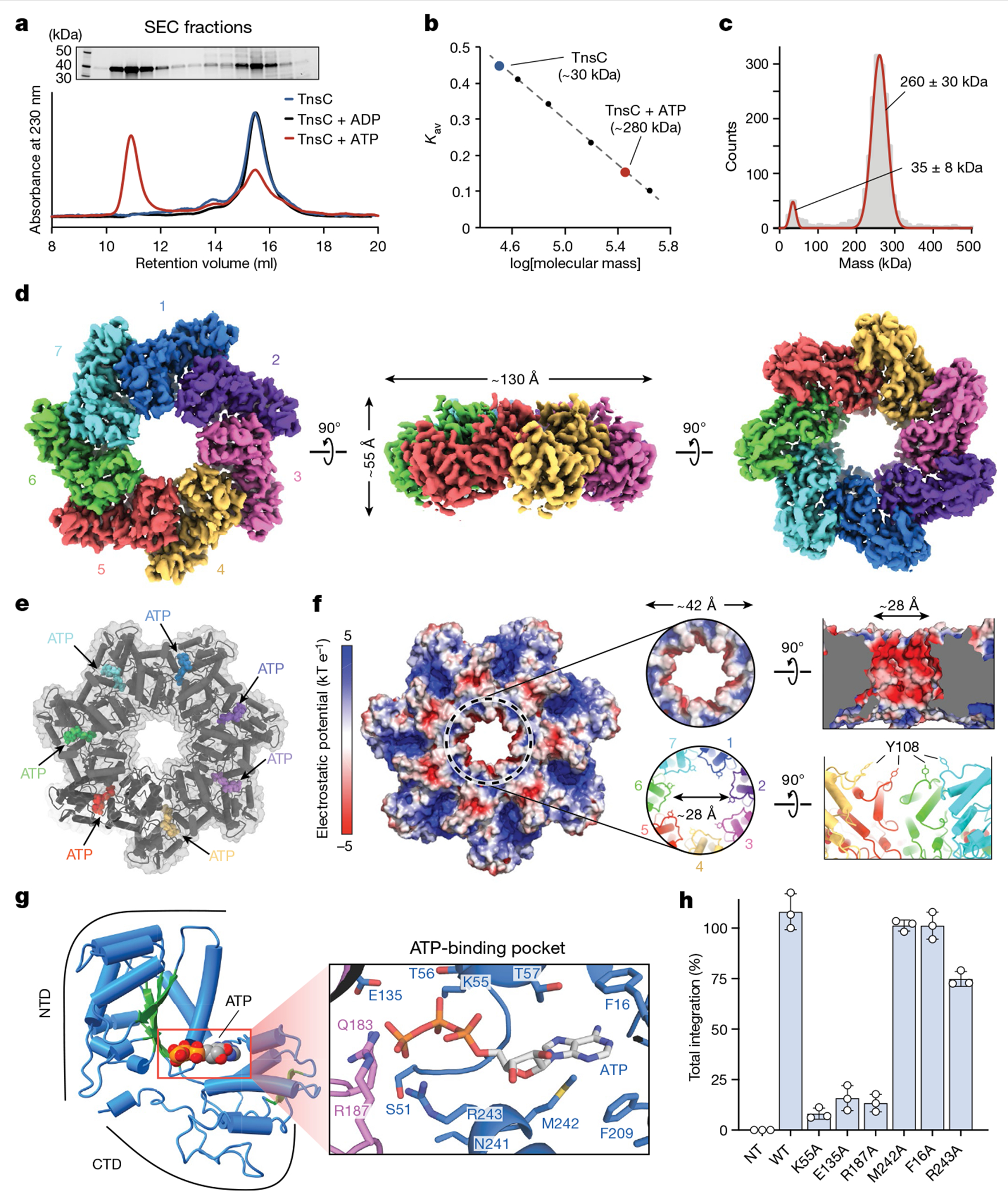
a, SEC profile of TnsC alone (blue) or in the presence of ADP (black) or ATP (red) (bottom). A high-molecular-weight oligomer is observed only in the presence of ATP. Top, SDS–PAGE analysis of SEC fractions. Gel source data are provided in Supplementary Fig. 1. b, SEC calibration curve with molecular weight standards. The estimated mass for the TnsC oligomer was about 280 kDa, which is compatible with a heptameric architecture. Kav, partition coefficient. c, iSCAMS analysis of a TnsC•ATP sample. d, Three orthogonal views of the final cryo-EM map for the TnsC•ATP heptamer. The overall dimensions are indicated in the side view (centre). e, Cartoon representation of TnsC heptamer from the refined model, configured as in d, with ATP molecules shown as coloured spheres. f, Electrostatic surface potential representation of TnsC heptamer, configured as in d. Right, a magnified view of the central pore is shown from a top and side view. The inner diameter (~28 Å) is defined in part by Tyr108 contributed by each monomer. g, Cartoon representation of a TnsC monomer from the refined model, with the NTD and CTD indicated. The central β-sheet characteristic of AAA+ domains is coloured in green, and the bound ATP molecule is shown in spheres representation. Right, a magnified view of the ATP-binding pocket, with residues labelled, h, RNA-guided transposition assays for WT TnsC and the indicated mutants within the ATP-binding pocket, as measured using qPCR. NT, non-targeting crRNA control. Data are shown as mean ± s.d. of n = 3 independent biological replicates.
