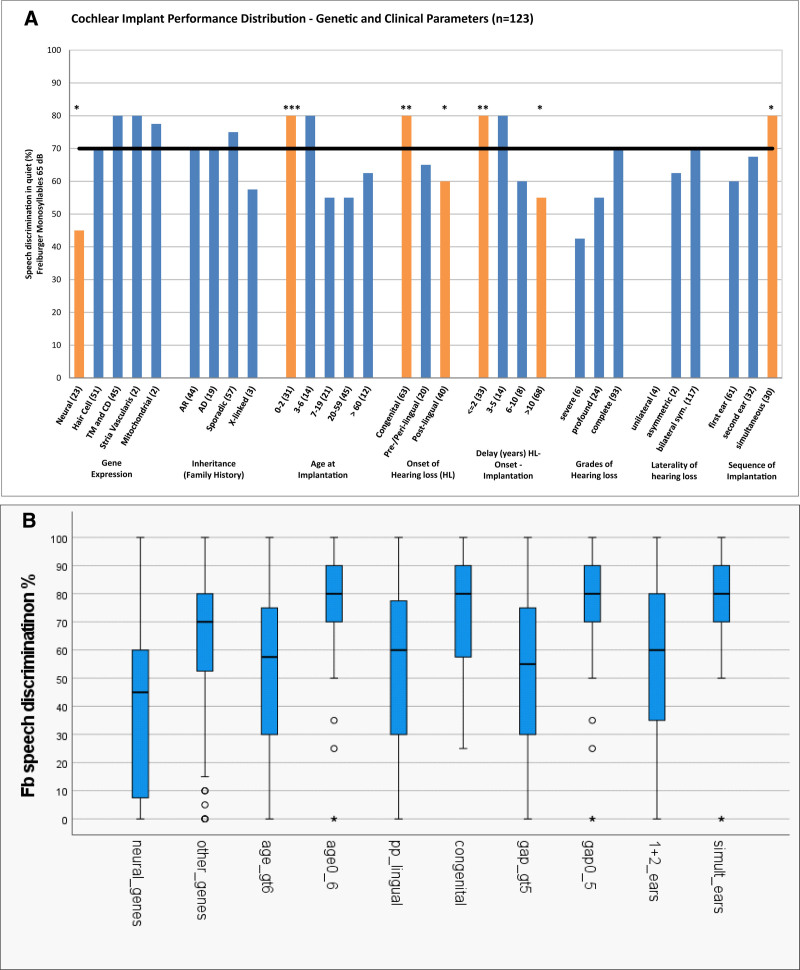
Fig. 5.
Cochlear implant performance including gene expression and demographic and clinical parameters according to the word recognition scores in the Freiburger monosyllabic speech intelligibility test at 65 dB SPL (WRS65) for 123 implanted ears. A, Cochlear implant performance for 30 categories. Demographic and clinical parameters consisted of inheritance based on the family history, onset of hearing loss, delay of implantation between the onset of hearing loss and cochlear implantation, grades of hearing loss, laterality of hearing loss and sequence of hearing loss. Statistical significance was determined with Fisher’s exact test (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.005, ***p < 0.0005). B, Cochlear implant performance for 10 broader genetic and clinical categories. Median value, interquartile range (IQR) and min/max estimates based on 1.5 IQR of word recognition scores. These represent five groups designated as (1) Gene expression: neural versus other nonneural genes; (2) age at implantation: 0–6 years (0-6y) of age versus age >6 years (gt 6y); (3) onset of hearing loss: congenital versus non-congenital (pre/peri/postlingual; pp_lingual); (4) implantation delay (gap): 0–5 years (0-5y) versus >5 years (gt 5y); (5) sequence of implantation: simultaneous bilateral implantation (simul_ears) versus subsequent bilateral or monaural only implantation (1 and 2 ears).