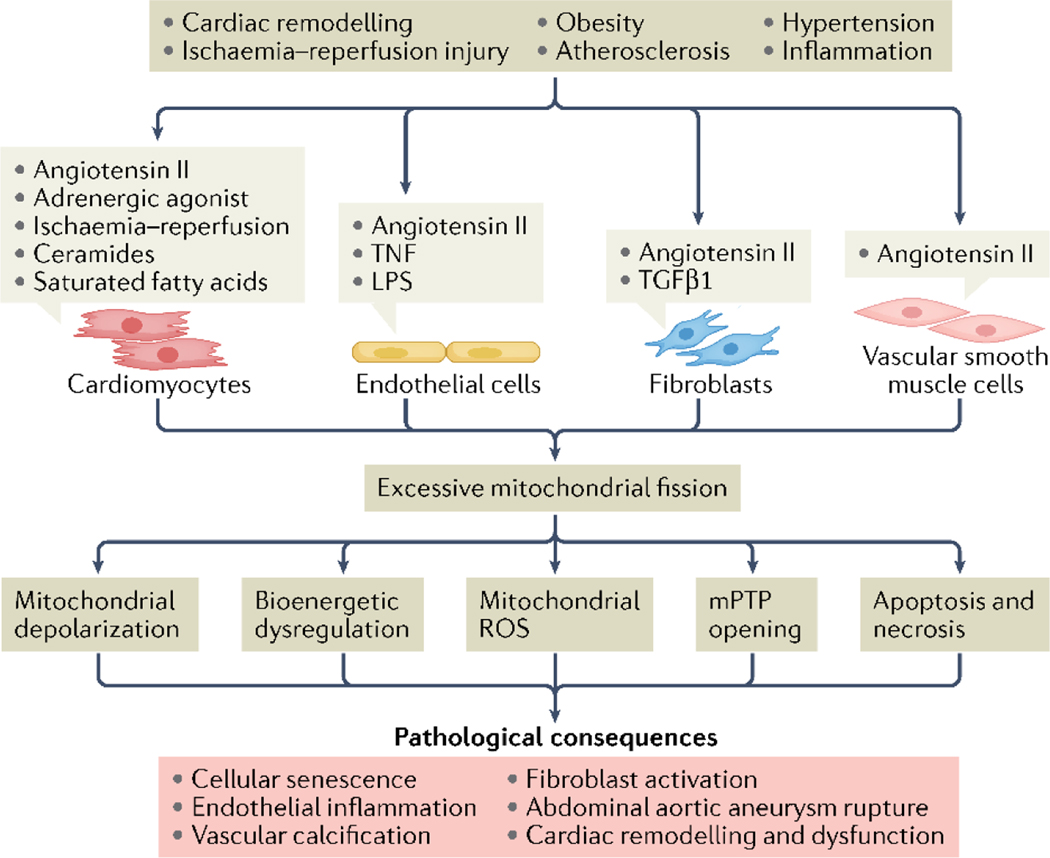
Fig. 4 |. Sustained mitochondrial fission promotes cardiovascular pathophysiology.
Several upstream signals shared and distinct among cardiac myocytes, endothelial cells, fibroblasts and vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMC) cause excessive mitochondrial fission, which culminates in organelle dysfunction and cell death. These effects directly promote cardiac and vascular pathophysiology across multiple disease models. AAA, abdominal aortic aneurysm; FA, fatty acids; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; mPTP, mitochondrial permeability transition pore; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TGF- β1, transforming growth factor β1; TNF, tumour necrosis factor.