Figure 5. Axon terminals from the LPO VGluT2 neurons establish asymmetric synapses on VTA TH, VGluT2, or VGaT neurons.
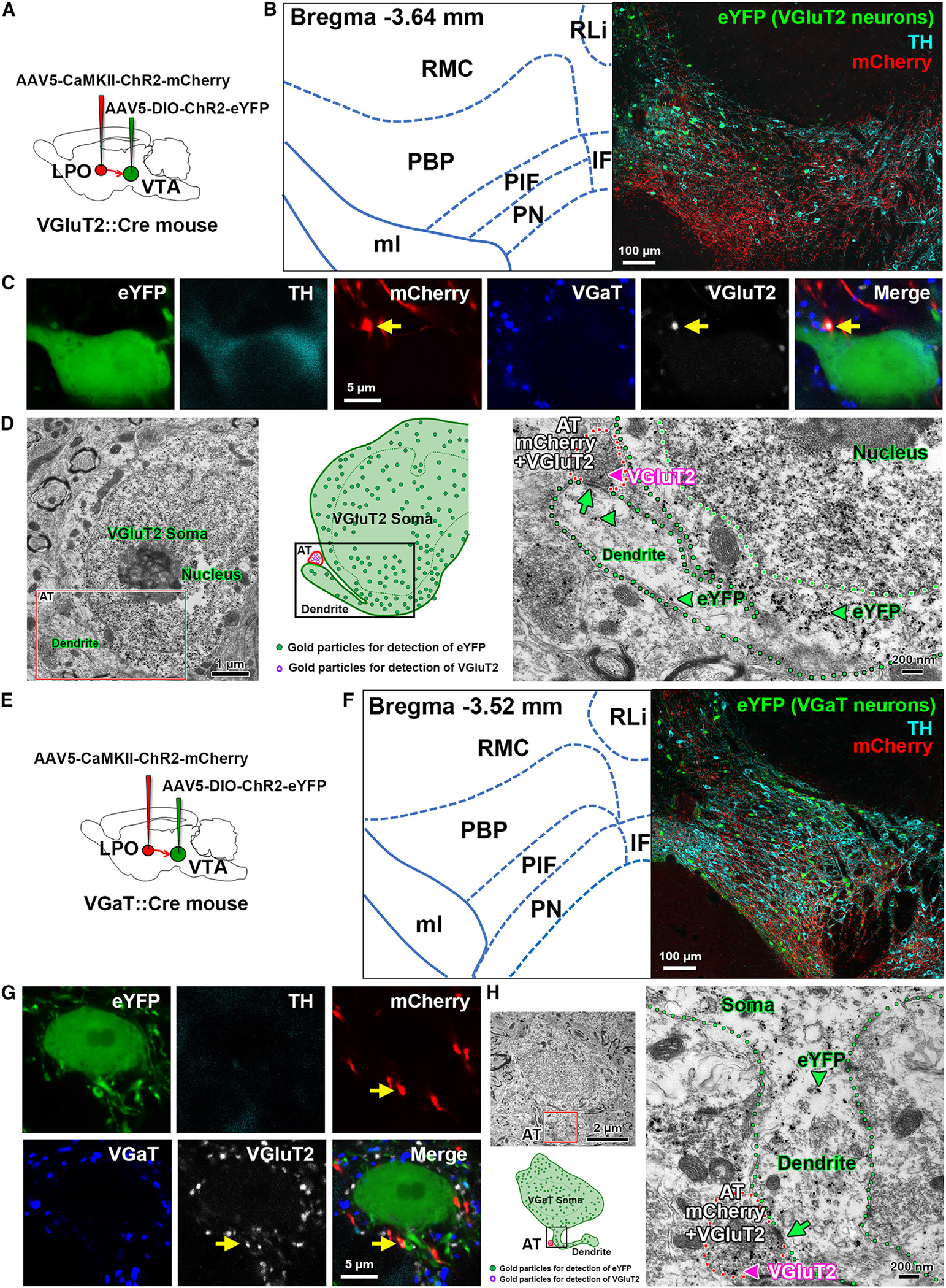
(A) Diagram of viral injection of AAV5-CaMKII-ChR2-mCherry into the LPO and AAV5-DIO-ChR2-eYFP into the VTA of vglut2:cre mice.
(B) Confocal micrograph of VTA at low magnification. TH, cyan; VGluT2-eYFP neurons, green; and mCherry fibers from LPO, red.
(C) Confocal micrographs at higher magnification showing the primary dendrite of a VTA TH and VGluT2-eYFP coexpressing neuron contacting an LPO-VGluT2 terminal coexpressing mCherry and VGluT2 protein (arrows).
(D) Electron micrographs and corresponding diagram showing a VGluT2 axon terminal (AT; red outlines) coexpressing mCherry (scattered dark material) and VGluT2 (pink arrowhead, gold particle) from an LPO neuron making an asymmetric synapse (green arrow) with the primary dendrite (green outline) of a VTA-VGluT2-eYFP neuron (eYFP detection by gold particles, green arrowheads).
(E) Diagram of viral injection of AAV5-CaMKII-ChR2-mCherry into the LPO and AAV5-DIO-ChR2-eYFP into the VTA of vgat:cre mice.
(F) Confocal micrograph of VTA at low magnification. TH, cyan; VGaT-eYFP neurons, green; and mCherry fibers from LPO, red.
(G) Confocal micrographs at higher magnification showing an LPO-VGluT2 terminal (coexpressing mCherry and VGluT2 protein, arrows) contacting the primary dendrite of a VTA VGaT-eYFP neuron.
