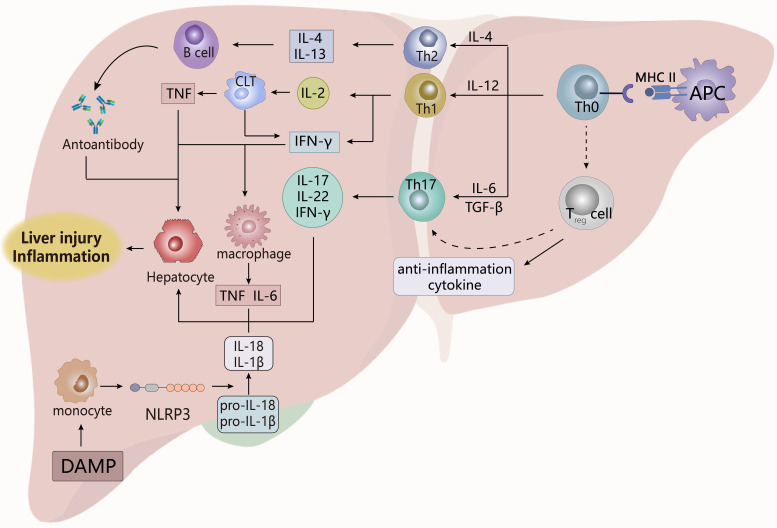
Figure 6.
The pathogenesis of AIH. The activation of T cells by antigen-presenting cells prompts them to differentiate into multiple cells, which act in tandem with B cells and innate immune cells by secreting different inflammatory factors to promote apoptosis and damage of liver cells, which eventually leads to the appearance of chronic hepatitis. Treg cells, regulatory T cells; DAMP, damage-related molecular patterns. APCs, antigen-presenting cells. CLT, Cytotoxic lymphoid T cells.