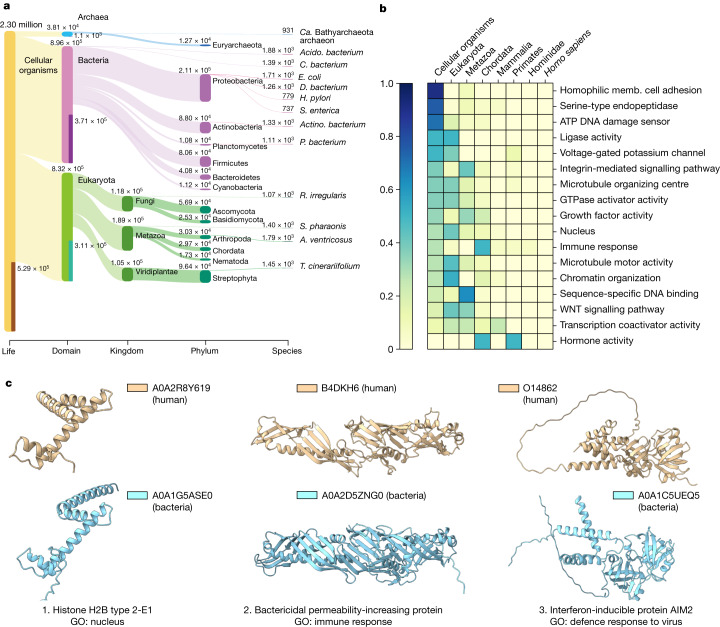
Fig. 3. Evolutionary distribution of clusters and human-centric cluster analysis.
a, Visualization of the LCA of all non-singleton clusters as a Sankey plot produced by Pavian. Only the largest 13 taxonomical nodes per rank are shown. b, The distribution of selected GO terms across the human lineage of the LCA based on the analysis of human protein-containing clusters (abundance is normalized per GO category). c, Three example structures from the human clusters that are conserved across humans and bacteria, among the eukaryote GO-annotated clusters. A histone protein with a nucleus GO annotation, which was found to be conserved at the cellular organism level and supports the previously reported evolutionary connection between eukaryotic and bacterial histones (left)26. The human innate immunity genes BPI (middle) and AIM2 (right) encode structurally similar proteins in bacterial species, highlighting the potential for cross-kingdom sharing of immunity-related proteins. Acido. bacterium, Acidobacteria bacterium; Actino. bacterium, Actinomycetia bacterium; ‘Ca. Bathyarchaeota archaeon’, ‘Candidatus Bathyarchaeota archaeon’; D. bacterium, Deltaproteobacteria bacterium; H. pylori, Helicobacter pylori; memb., membrane; P. bacterium, Planctomycetes bacterium; R. irregularis, Rhizophagus irregularis; S. enterica, Salmonella enterica; T. cinerariifolium, Tanacetum cinerariifolium.